Polish–Muscovite War (1609–1618) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Polish–Russian War of 1609–1618, also known as the Polish–Muscovite War or the ''Dimitriads'', was a conflict fought between the
ImageSize = width:500 height:100
PlotArea = left:65 right:15 bottom:20 top:5
AlignBars = justify
Colors =
id:godunovb value:rgb(0.99215,0.8,0.54)
id:godunovf value:rgb(1,0.7019,0)
id:dimitryi value:rgb(1,1,0)
id:szhujskiy value:rgb(1,1,0.702)
id:vladislav value:rgb(1,0.922,0.384)
id:romanov value:rgb(1,0.922,0.675)
Period = from:1600 till:1615
TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal
ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:1 start:1600
PlotData=
align:center textcolor:black fontsize:8 mark:(line,black) width:35 shift:(0,-5)
from:start till: 1605 text:"
In the late 16th and early 17th centuries,  In late 1600, a Polish
In late 1600, a Polish
 For most of the 17th century, Sigismund III was occupied with internal problems of his own, like the Nobles' Rebellion in the Commonwealth and the wars with Sweden and in Moldavia. However, the impostor
For most of the 17th century, Sigismund III was occupied with internal problems of his own, like the Nobles' Rebellion in the Commonwealth and the wars with Sweden and in Moldavia. However, the impostor  Dmitry attracted a number of followers, formed a small army, and, supported by approximately 3500 soldiers of the Commonwealth magnates' private armies and the mercenaries bought by Dmitriy's own cash, rode to Russia in June 1604. Some of Godunov's other enemies, including approximately 2,000 southern
Dmitry attracted a number of followers, formed a small army, and, supported by approximately 3500 soldiers of the Commonwealth magnates' private armies and the mercenaries bought by Dmitriy's own cash, rode to Russia in June 1604. Some of Godunov's other enemies, including approximately 2,000 southern
 Tsar Vasili Shuyski was unpopular and weak in Russia and his reign was far from stable. He was perceived as anti-Polish; he had led the coup against the first False Dmitry, killing over 500 Polish soldiers in Moscow and imprisoning a Polish envoy. The civil war raged on, as in 1607 the False Dmitry II appeared, again supported by some Polish
Tsar Vasili Shuyski was unpopular and weak in Russia and his reign was far from stable. He was perceived as anti-Polish; he had led the coup against the first False Dmitry, killing over 500 Polish soldiers in Moscow and imprisoning a Polish envoy. The civil war raged on, as in 1607 the False Dmitry II appeared, again supported by some Polish
 In 1609 the Zebrzydowski Rebellion ended when Tsar Vasili signed a military alliance with
In 1609 the Zebrzydowski Rebellion ended when Tsar Vasili signed a military alliance with
/ref> Some Russian boyars assured Sigismund of their support by offering the throne to his son, Prince Wladislaus IV of Poland, Władysław. Previously, Sigismund had been unwilling to commit the majority of Polish forces or his time to the internal conflict in Russia, but in 1609 those factors made him re-evaluate and drastically change his policy. Although many Polish nobles and soldiers were fighting for the second False Dmitry at the time, Sigismund III and the troops under his command did not support Dimitriy for the throne – Sigismund wanted Russia himself. The entry of Sigismund into Russia caused the majority of the Polish supporters of False Dmitry II to desert him and contributed to his defeat. A series of subsequent disasters induced False Dmitry II to flee his camp disguised as a peasant and to go to Kostroma together with Marina. Dmitry made another unsuccessful attack on Moscow, and, supported by the Not all of the Commonwealth attacks were successful. An early attack, led by Hetman
Not all of the Commonwealth attacks were successful. An early attack, led by Hetman
 Hetman Żółkiewski, whose only other choice was mutiny, decided to follow the king's orders and left Smolensk in 1610, leaving only a smaller force necessary to continue the siege. With Cossack reinforcements, he marched on Moscow. However, as he feared and predicted, as the Polish–Lithuanian forces pressed eastwards, ravaging Russian lands, and as Sigismund's lack of willingness to compromise became more and more apparent, many supporters of the Poles and of the second False Dmitry left the pro-Polish camp and turned to Shuyski's anti-Polish faction.
Hetman Żółkiewski, whose only other choice was mutiny, decided to follow the king's orders and left Smolensk in 1610, leaving only a smaller force necessary to continue the siege. With Cossack reinforcements, he marched on Moscow. However, as he feared and predicted, as the Polish–Lithuanian forces pressed eastwards, ravaging Russian lands, and as Sigismund's lack of willingness to compromise became more and more apparent, many supporters of the Poles and of the second False Dmitry left the pro-Polish camp and turned to Shuyski's anti-Polish faction.
 Russian forces under Grigory Voluyev were coming to relieve Smolensk and fortified the fort at Tsaryovo-Zaymishche (Carowo, Cariewo, Tsarovo–Zajmiszcze) to bar the Poles' advance on Moscow. The Siege of Tsaryovo began on 24 June. However, the Russians were not prepared for a long siege and had little food and water inside the fort. Voluyev sent word for Dmitry Shuyski (Tsar Shuyski's brother) to come to their aid and lift the siege. Shuyski's troops marched for Tsaryovo, not by the direct route, but round-about through Klushino, hoping to come to Tsaryovo by the back route. Shuyski received aid from Swedish forces under the command of Jacob Pontusson De la Gardie.
Żółkiewski learned of Shuyski's relief force and divided his troops to meet the Russians before they could come to Tsaryovo and lift the siege. He left at night so that Voluyev would not notice his absence. The combined Russian and Swedish armies were defeated on 4 July 1610 at the
Russian forces under Grigory Voluyev were coming to relieve Smolensk and fortified the fort at Tsaryovo-Zaymishche (Carowo, Cariewo, Tsarovo–Zajmiszcze) to bar the Poles' advance on Moscow. The Siege of Tsaryovo began on 24 June. However, the Russians were not prepared for a long siege and had little food and water inside the fort. Voluyev sent word for Dmitry Shuyski (Tsar Shuyski's brother) to come to their aid and lift the siege. Shuyski's troops marched for Tsaryovo, not by the direct route, but round-about through Klushino, hoping to come to Tsaryovo by the back route. Shuyski received aid from Swedish forces under the command of Jacob Pontusson De la Gardie.
Żółkiewski learned of Shuyski's relief force and divided his troops to meet the Russians before they could come to Tsaryovo and lift the siege. He left at night so that Voluyev would not notice his absence. The combined Russian and Swedish armies were defeated on 4 July 1610 at the  After the news of Klushino spread, support for Tsar Shuyski almost completely evaporated. Żółkiewski soon convinced the Russian units at Tsaryovo, which were much stronger than the ones at Kłuszyn, to capitulate and to swear an oath of loyalty to Władysław. Then he incorporated them into his army and moved towards Moscow. In August 1610 many Russian
After the news of Klushino spread, support for Tsar Shuyski almost completely evaporated. Żółkiewski soon convinced the Russian units at Tsaryovo, which were much stronger than the ones at Kłuszyn, to capitulate and to swear an oath of loyalty to Władysław. Then he incorporated them into his army and moved towards Moscow. In August 1610 many Russian  In the meantime, Żółkiewski and the second False Dmitriy, formerly reluctant allies, began to part ways. The second False Dmitry had lost much of his influence over the Polish court, and Żółkiewski would eventually try to drive Dmitry from the capital. Żółkiewski soon began manoeuvring for a tsar of Polish origin, particularly the 15-year-old Prince Władysław. The boyars had offered the throne to Władysław at least twice, in the hopes of having the
In the meantime, Żółkiewski and the second False Dmitriy, formerly reluctant allies, began to part ways. The second False Dmitry had lost much of his influence over the Polish court, and Żółkiewski would eventually try to drive Dmitry from the capital. Żółkiewski soon began manoeuvring for a tsar of Polish origin, particularly the 15-year-old Prince Władysław. The boyars had offered the throne to Władysław at least twice, in the hopes of having the
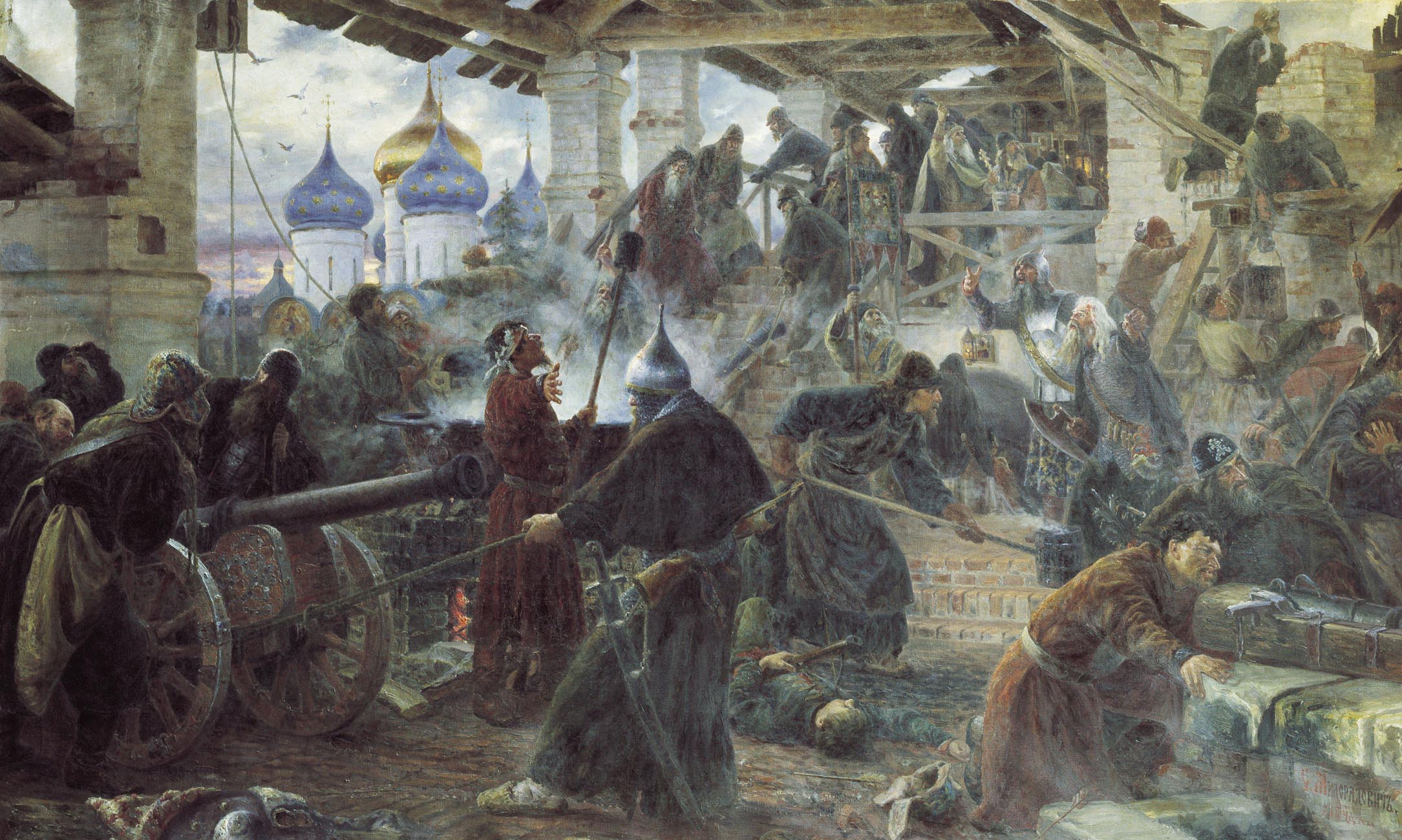
 A 1611 uprising in Moscow against the Polish garrison marked the end of Russian tolerance for the Commonwealth intervention. The citizens of Moscow had voluntarily participated in the coup in 1606, killing 500 Polish soldiers. Now, ruled by the Poles, they once again revolted. The Moscow burghers took over the munition store, but Polish troops defeated the first wave of attackers, and the fighting resulted in a large fire that consumed part of Moscow. From July onward the situation of the Commonwealth forces became grave, as the uprising turned into a siege of the Polish-held Kremlin. Reportedly, the Poles had imprisoned the leader of the Orthodox Church,
A 1611 uprising in Moscow against the Polish garrison marked the end of Russian tolerance for the Commonwealth intervention. The citizens of Moscow had voluntarily participated in the coup in 1606, killing 500 Polish soldiers. Now, ruled by the Poles, they once again revolted. The Moscow burghers took over the munition store, but Polish troops defeated the first wave of attackers, and the fighting resulted in a large fire that consumed part of Moscow. From July onward the situation of the Commonwealth forces became grave, as the uprising turned into a siege of the Polish-held Kremlin. Reportedly, the Poles had imprisoned the leader of the Orthodox Church,  Russian reinforcements under Prince Pozharsky eventually starved the Commonwealth garrison (there were reports of
Russian reinforcements under Prince Pozharsky eventually starved the Commonwealth garrison (there were reports of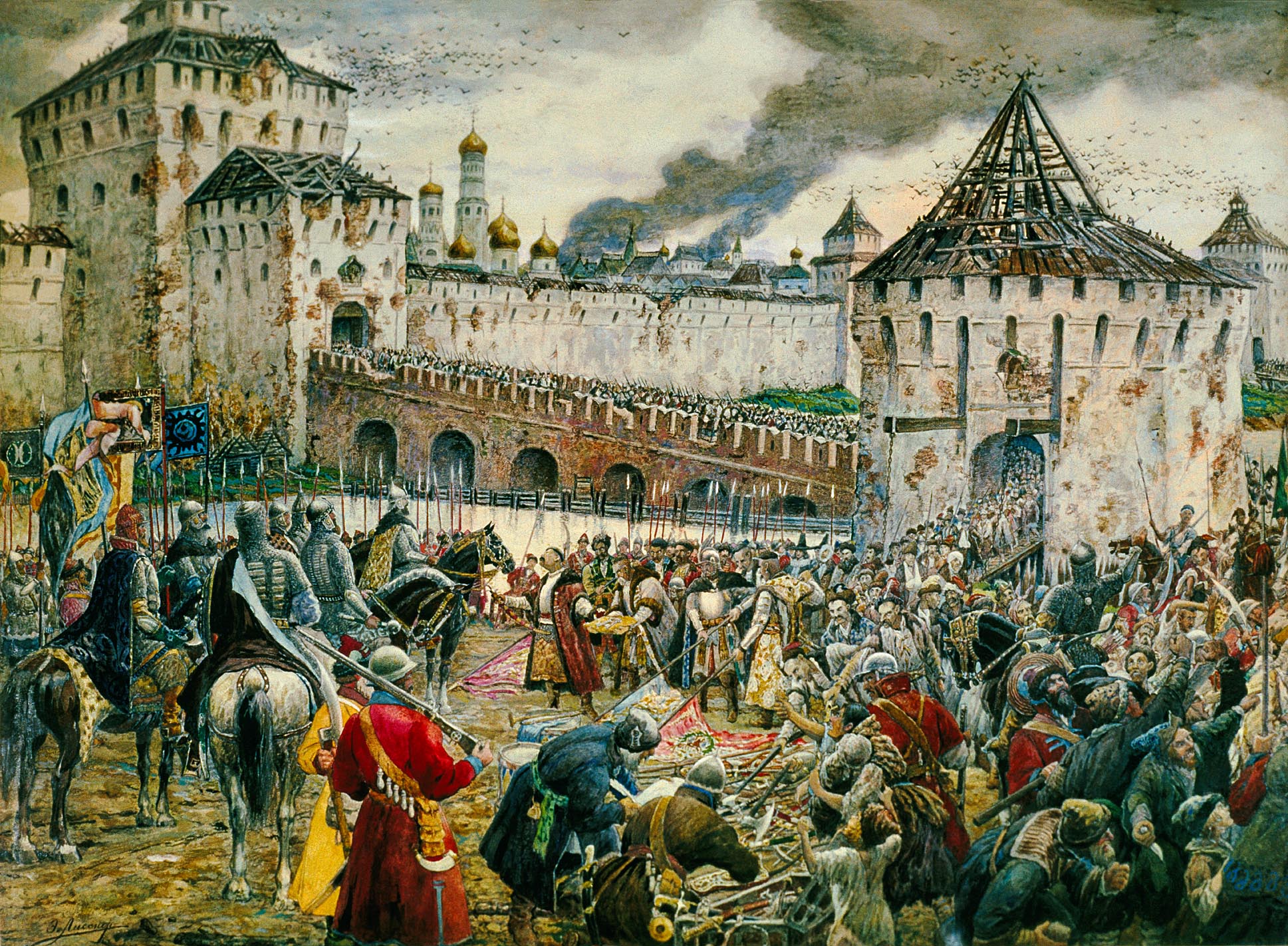  On 2 June 1611 Smolensk had finally fallen to the Poles. After enduring 20 months of siege, two harsh winters and dwindling food supplies, the Russians in Smolensk finally reached their limit as the Polish–Lithuanian troops broke through the city gates. The Polish army, advised by the runaway traitor Andrei Dedishin, discovered a weakness in the fortress defenses, and on 13 June 1611 Cavalier of Malta Bartłomiej Nowodworski inserted a mine into a sewer canal. The explosion created a large breach in the fortress walls. The fortress fell on the same day. The remaining 3,000 Russian defenders took refuge in the Assumption Cathedral and blew themselves up with stores of gunpowder to avoid death at the hands of the invaders. Although it was a blow to lose Smolensk, the defeat freed up Russian troops to fight the Commonwealth in Moscow, and the Russian commander at Smolensk, Mikhail Borisovich Shein, was considered a hero for holding out as long as he had. He was captured at Smolensk and remained a prisoner of Poland–Lithuania for the next nine years.
On 2 June 1611 Smolensk had finally fallen to the Poles. After enduring 20 months of siege, two harsh winters and dwindling food supplies, the Russians in Smolensk finally reached their limit as the Polish–Lithuanian troops broke through the city gates. The Polish army, advised by the runaway traitor Andrei Dedishin, discovered a weakness in the fortress defenses, and on 13 June 1611 Cavalier of Malta Bartłomiej Nowodworski inserted a mine into a sewer canal. The explosion created a large breach in the fortress walls. The fortress fell on the same day. The remaining 3,000 Russian defenders took refuge in the Assumption Cathedral and blew themselves up with stores of gunpowder to avoid death at the hands of the invaders. Although it was a blow to lose Smolensk, the defeat freed up Russian troops to fight the Commonwealth in Moscow, and the Russian commander at Smolensk, Mikhail Borisovich Shein, was considered a hero for holding out as long as he had. He was captured at Smolensk and remained a prisoner of Poland–Lithuania for the next nine years.
 After the fall of Smolensk, the Russo-Polish border remained relatively quiet for the next few years. However, no official treaty was signed. Sigismund, criticized by the
After the fall of Smolensk, the Russo-Polish border remained relatively quiet for the next few years. However, no official treaty was signed. Sigismund, criticized by the  While both countries were shaken by internal strife, many smaller factions thrived. Polish
While both countries were shaken by internal strife, many smaller factions thrived. Polish
 Eventually the Commonwealth Sejm voted to raise the funds necessary to resume large scale military operations. The final attempt by Sigismund and Władysław to gain the throne was a new campaign launched on 6 April 1617. Władysław was the nominal commander, but it was hetman Chodkiewicz who had actual control over the army. In October, the towns of
Eventually the Commonwealth Sejm voted to raise the funds necessary to resume large scale military operations. The final attempt by Sigismund and Władysław to gain the throne was a new campaign launched on 6 April 1617. Władysław was the nominal commander, but it was hetman Chodkiewicz who had actual control over the army. In October, the towns of
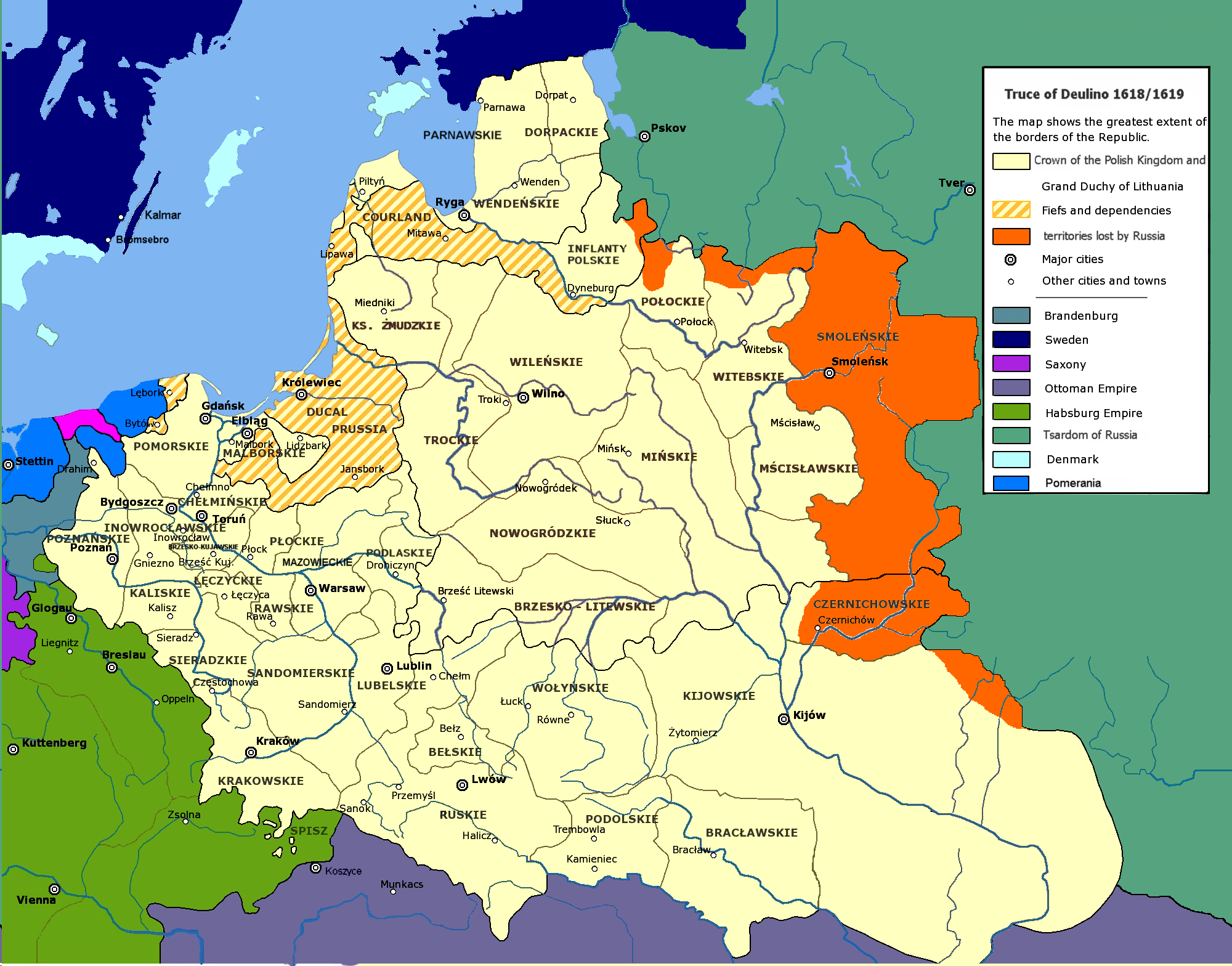 In the end, Sigismund did not succeed in becoming tsar or in securing the throne for Władysław, but he was able to expand the Commonwealth's territory. During his reign Poland-Lithuania was the largest and most populous country in
In the end, Sigismund did not succeed in becoming tsar or in securing the throne for Władysław, but he was able to expand the Commonwealth's territory. During his reign Poland-Lithuania was the largest and most populous country in
 The story of the Dymitriads and False Dimitrys proved useful to future generations of rulers and politicians in Poland and Russia, and a distorted version of the real events gained much fame in Russia, as well as in Poland. In Poland the Dmitriads campaign is remembered as the height of the Polish Golden Age, the time Poles captured Moscow, something that even four million troops from
The story of the Dymitriads and False Dimitrys proved useful to future generations of rulers and politicians in Poland and Russia, and a distorted version of the real events gained much fame in Russia, as well as in Poland. In Poland the Dmitriads campaign is remembered as the height of the Polish Golden Age, the time Poles captured Moscow, something that even four million troops from
Polacy na Kremlu
Tygodnik "Wprost", Nr 1182 (31 lipca 2005), , accessed on 29 July 2005 *
Polish occupation of Russia
!--404 now--> {{DEFAULTSORT:Polish-Muscovite War (1605-18) 1600s in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth 1600s in Russia 1610s in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth 1610s in Russia 17th-century conflicts Invasions of Russia Wars involving Russia Wars involving the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Polish–Russian wars Warfare of the Early Modern period Wars of succession involving the states and peoples of Europe Time of Troubles
Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I i ...
and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
together with Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporoz ...
from 1609 to 1618.
Russia had been experiencing the Time of Troubles
The Time of Troubles (russian: Смутное время, ), or Smuta (russian: Смута), was a period of political crisis during the Tsardom of Russia which began in 1598 with the death of Fyodor I (Fyodor Ivanovich, the last of the Rurik dy ...
since the death of Tsar Feodor I
Fyodor I Ivanovich (russian: Фёдор I Иванович) or Feodor I Ioannovich (russian: Феодор I Иоаннович; 31 May 1557 – 17 January (NS) 1598), also known as Feodor the Bellringer (russian: Феодор Звонарь), ...
in 1598, causing political instability Political decay is a political theory, originally described by Samuel P. Huntington, which describes how chaos and disorder can arise from social modernization increasing more rapidly than political and institutional modernization. Huntington provi ...
and a violent succession crisis A succession crisis is a crisis that arises when an order of succession fails, for example when a king dies without an indisputable heir. It may result in a war of succession.
Examples include (see List of wars of succession):
*Multiple periods dur ...
upon the extinction of the Rurik dynasty
The Rurik dynasty ( be, Ру́рыкавічы, Rúrykavichy; russian: Рю́риковичи, Ryúrikovichi, ; uk, Рю́риковичі, Riúrykovychi, ; literally "sons/scions of Rurik"), also known as the Rurikid dynasty or Rurikids, was ...
, and was ravaged by the major famine of 1601 to 1603. Poland exploited Russia's civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
s when members of the Polish ''szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in the ...
'' aristocracy began influencing Russian boyar
A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the Feudalism, feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Kievan Rus', Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria, Russian nobility, Russia, Boyars of Moldavia and Wallachia, Wallachia and ...
s and supporting False Dmitris for the title of Tsar of Russia
This is a list of all reigning monarchs in the history of Russia. It includes the princes of medieval Rus′ state (both centralised, known as Kievan Rus', Kievan Rus′ and feudal, when the political center moved northeast to Grand Duke of Vl ...
against the crowned Boris Godunov
Borís Fyodorovich Godunóv (; russian: Борис Фёдорович Годунов; 1552 ) ruled the Tsardom of Russia as ''de facto'' regent from c. 1585 to 1598 and then as the first non-Rurikid tsar from 1598 to 1605. After the end of his ...
and Vasili IV Shuysky. In 1605, Polish nobles conducted a series of skirmishes until the death of False Dmitry I
False Dmitry I ( rus, Лжедмитрий I, Lzhedmitriy I) (or Pseudo-Demetrius I) reigned as the Tsar of Russia from 10 June 1605 until his death on 17 May 1606 under the name of Dmitriy Ivanovich ( rus, Дмитрий Иванович). A ...
in 1606, and invaded again in 1607 until Russia formed a military alliance with Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
two years later. Polish King Sigismund Sigismund (variants: Sigmund, Siegmund) is a German proper name, meaning "protection through victory", from Old High German ''sigu'' "victory" + ''munt'' "hand, protection". Tacitus latinises it '' Segimundus''. There appears to be an older form of ...
declared war
A declaration of war is a formal act by which one state announces existing or impending war activity against another. The declaration is a performative speech act (or the signing of a document) by an authorized party of a national government, i ...
on Russia in response in 1609, aiming to gain territorial concessions and weaken Sweden's ally, winning many early victories such as the Battle of Klushino
The Battle of Klushino, or the Battle of Kłuszyn, was fought on 4 July 1610, between forces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia during the Polish–Muscovite War, part of Russia's Time of Troubles. The battle occ ...
. In 1610, Polish forces entered Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
and Sweden withdrew from the military alliance with Russia, instead triggering the Ingrian War
The Ingrian War ( sv, Ingermanländska kriget) between the Swedish Empire and the Tsardom of Russia lasted between 1610 and 1617. It can be seen as part of Russia's Time of Troubles and is mainly remembered for the attempt to put a Swedish duke ...
.
Sigismund's son, the Prince Władysław of Poland, was elected tsar by the Seven Boyars
The Seven Boyars (russian: link=no, Семибоярщина, the Russian term indicating "Rule of the Seven Boyars" or "the Deeds of the Seven Boyars") were a group of Russian nobles who deposed Tsar Vasily Shuisky on 17 July 1610 and, later that ...
in September 1610, but Sigismund refused to allow his son to become the new tsar unless the Muscovites agreed to convert to Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, with the pro-Polish boyars ending their support for the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In 1611, Kuzma Minin
Kuzma (Kozma) Minin (; full name Kuzma Minich Zakhariev-Sukhoruky, born late 1570s - died 1616) was a Russian merchant from Nizhny Novgorod, Russia, who, together with Prince Dmitry Pozharsky, became a national hero for his role in defending the ...
and Prince Dmitry Pozharsky
Dmitry Mikhaylovich Pozharsky ( rus, Дми́трий Миха́йлович Пожа́рский, p=ˈdmʲitrʲɪj mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪtɕ pɐˈʐarskʲɪj; 17 October 1577 – 30 April 1642) was a Russian prince known for his military leadershi ...
formed a new army to launch a popular revolt
This is a chronological list of conflicts in which peasants played a significant role.
Background
The history of peasant wars spans over two thousand years. A variety of factors fueled the emergence of the peasant revolt phenomenon, including:
...
against the Polish occupation. The Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
captured Smolensk in June 1611 but began to retreat after they were ousted from Moscow in September 1612. Michael Romanov, the son of Patriarch Filaret of Moscow
Feodor Nikitich Romanov (russian: Фео́дор Ники́тич Рома́нов, ; 1553 – 1 October 1633) was a Russian boyar who after temporary disgrace rose to become patriarch of Moscow as Filaret (russian: Филаре́т, ), and bec ...
, was elected Tsar of Russia in 1613, beginning the Romanov dynasty
The House of Romanov (also transcribed Romanoff; rus, Романовы, Románovy, rɐˈmanəvɨ) was the reigning imperial house of Russia from 1613 to 1917. They achieved prominence after the Tsarina, Anastasia Romanova, was married to ...
and ending the Time of Troubles. With little military action between 1612 and 1617, the war finally ended in 1618 with the Truce of Deulino
The Truce of Deulino (also known as Peace or Treaty of Dywilino) concluded the Polish–Muscovite War (1609–1618) between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia. It was signed on 11 December 1618 and took effect on 4 Jan ...
, which granted the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth certain territorial concessions but preserved Russia's independence.
The war was the first major sign of the rivalry and uneasy relations between Poland and Russia which last to this day. Its aftermath had a long-lasting impact on Russian society, creating the negative stereotype of Poland in Russia and, most notably, giving rise to the Romanov dynasty
The House of Romanov (also transcribed Romanoff; rus, Романовы, Románovy, rɐˈmanəvɨ) was the reigning imperial house of Russia from 1613 to 1917. They achieved prominence after the Tsarina, Anastasia Romanova, was married to ...
which ruled Russia for three centuries until the February Revolution
The February Revolution ( rus, Февра́льская револю́ция, r=Fevral'skaya revolyutsiya, p=fʲɪvˈralʲskəjə rʲɪvɐˈlʲutsɨjə), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and somet ...
in 1917. It also left a noticeable mark on Russian culture, with renowned writers and composers portraying the war in works such as ''Boris Godunov'' (play) by Alexander Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (; rus, links=no, Александр Сергеевич ПушкинIn pre-Revolutionary script, his name was written ., r=Aleksandr Sergeyevich Pushkin, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈpuʂkʲɪn, ...
(adapted into an opera by Modest Mussorgsky
Modest Petrovich Mussorgsky ( rus, link=no, Модест Петрович Мусоргский, Modest Petrovich Musorgsky , mɐˈdɛst pʲɪˈtrovʲɪtɕ ˈmusərkskʲɪj, Ru-Modest Petrovich Mussorgsky version.ogg; – ) was a Russian compo ...
), ''A Life for the Tsar
''A Life for the Tsar'' ( rus, "Жизнь за царя", italic=yes, Zhizn za tsarya ) is a "patriotic-heroic tragic opera" in four acts with an epilogue by Mikhail Glinka. During the Soviet era the opera was known under the name ''Ivan Susanin' ...
'' by Mikhail Glinka
Mikhail Ivanovich Glinka ( rus, link=no, Михаил Иванович Глинка, Mikhail Ivanovich Glinka., mʲɪxɐˈil ɪˈvanəvʲɪdʑ ˈɡlʲinkə, Ru-Mikhail-Ivanovich-Glinka.ogg; ) was the first Russian composer to gain wide recogni ...
, '' Pan Voyevoda'' by Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
Nikolai Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov . At the time, his name was spelled Николай Андреевичъ Римскій-Корсаковъ. la, Nicolaus Andreae filius Rimskij-Korsakov. The composer romanized his name as ''Nicolas Rimsk ...
as well as films '' Minin and Pozharsky'' and '' 1612''.
Names of the war
The conflict is often referred to by different names, most commonly the ''Russo–Polish War'', with the term Russia replacing the term Muscovy. In Polishhistoriography
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians ha ...
, the wars are usually referred to as the '' Dimitriads'': the ''First Dymitriad'' (1605–1606) and ''Second Dymitriad'' (1607–1609) and the ''Polish–Muscovite War'' (1609–1618), which can subsequently be divided into two wars of 1609–1611 and 1617–1618, and may or may not include the 1617–1618 campaign, which is sometimes referred to as ''Chodkiewicz uscoviteCampaign''. According to Russian historiography, the chaotic events of the war fall into the "Time of Troubles
The Time of Troubles (russian: Смутное время, ), or Smuta (russian: Смута), was a period of political crisis during the Tsardom of Russia which began in 1598 with the death of Fyodor I (Fyodor Ivanovich, the last of the Rurik dy ...
". The conflict with Poles is commonly called the ''Polish Invasion'', ''Polish Intervention'', or more specifically the ''Polish Intervention of the Early Seventeenth Century''.
Prelude to the war
Boris Godunov
Borís Fyodorovich Godunóv (; russian: Борис Фёдорович Годунов; 1552 ) ruled the Tsardom of Russia as ''de facto'' regent from c. 1585 to 1598 and then as the first non-Rurikid tsar from 1598 to 1605. After the end of his ...
" color:godunovb
# fontsize:6
from:1605 till: 1605.5 text:"Feodor II
Fyodor II Borisovich Godunov (russian: Фёдор II Борисович Годунов) (1589 – 20 June 1605) was tsar of Russia during the spring of 1605, at the beginning of the Time of Troubles.
Life
Fyodor II was born in Moscow, the son a ...
" shift:(-30,10) color:godunovf
from:1605.5 till: 1606.4 text:"False Dmitry I
False Dmitry I ( rus, Лжедмитрий I, Lzhedmitriy I) (or Pseudo-Demetrius I) reigned as the Tsar of Russia from 10 June 1605 until his death on 17 May 1606 under the name of Dmitriy Ivanovich ( rus, Дмитрий Иванович). A ...
" shift:(17,-15) color:dimitryi
# fontsize:8
from:1606.4 till: 1610.7 text:" Vasili IV" color:szhujskiy
from:1610.7 till: 1613 text:" Vladislav IV" color:vladislav
from:1613 till:end text:"Michael I Michael I may refer to:
* Pope Michael I of Alexandria, Coptic Pope of Alexandria and Patriarch of the See of St. Mark in 743–767
* Michael I Rhangabes, Byzantine Emperor (died in 844)
* Michael I Cerularius, Patriarch Michael I of Constantinopl ...
" color:romanov
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
was in a state of political and economic crisis. After the death of Tsar Ivan IV
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (russian: Ива́н Васи́льевич; 25 August 1530 – ), commonly known in English as Ivan the Terrible, was the grand prince of Moscow from 1533 to 1547 and the first Tsar of all Russia from 1547 to 1584.
Ivan ...
("the Terrible") in 1584, and the death of his son Dimitri in 1591, several factions competed for the tsar's throne. In 1598, Boris Godunov
Borís Fyodorovich Godunóv (; russian: Борис Фёдорович Годунов; 1552 ) ruled the Tsardom of Russia as ''de facto'' regent from c. 1585 to 1598 and then as the first non-Rurikid tsar from 1598 to 1605. After the end of his ...
was crowned to the Russian throne, marking the end of the centuries long rule of the Rurik dynasty
The Rurik dynasty ( be, Ру́рыкавічы, Rúrykavichy; russian: Рю́риковичи, Ryúrikovichi, ; uk, Рю́риковичі, Riúrykovychi, ; literally "sons/scions of Rurik"), also known as the Rurikid dynasty or Rurikids, was ...
. While his policies were rather moderate and well-intentioned, his rule was marred by the general perception of its questionable legitimacy and allegations of his involvement in orchestrating the assassination of Dimitri. While Godunov managed to put the opposition to his rule under control, he did not manage to crush it completely. To add to his troubles, the first years of the 17th century were exceptionally cold. The drop in temperature was felt all over the world and was most likely caused by a severe eruption of a volcano in South America. In Russia, it resulted in a great famine that swept through the country from 1601 to 1603.
 In late 1600, a Polish
In late 1600, a Polish diplomatic mission
A diplomatic mission or foreign mission is a group of people from a state or organization present in another state to represent the sending state or organization officially in the receiving or host state. In practice, the phrase usually deno ...
led by Chancellor Lew Sapieha
Lew Sapieha ( lt, Leonas Sapiega; be, Леў Сапега or Lieŭ Sapieha; 4 April 1557 – 7 July 1633) was a nobleman and statesman of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. He became Great Secretary of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1580, Gr ...
with Eliasz Pielgrzymowski and Stanisław Warszycki arrived in Moscow and proposed an alliance between the Commonwealth and Russia, which would include a future personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
. They proposed that after one monarch's death without heirs, the other would become the ruler of both countries. However, Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
Godunov declined the union proposal and settled on extending the Treaty of Jam Zapolski
The Truce or Treaty of Yam-Zapolsky (Ям-Запольский) or Jam Zapolski, signed on 15 January 1582 between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia, was one of the treaties that ended the Livonian War. It followed t ...
, which ended the Lithuanian wars of the 16th century, by 22 years (to 1622).
Sigismund and the Commonwealth magnates knew full well that they were not capable of any serious invasion of Russia; the Commonwealth army was too small, its treasury always empty, and the war lacked popular support. However, as the situation in Russia deteriorated, Sigismund and many Commonwealth magnate
The magnate term, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders, or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
s, especially those with estates and forces near the Russian border, began to look for a way to profit from the chaos and weakness of their eastern neighbour. This proved easy, as in the meantime many Russian boyar
A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the Feudalism, feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Kievan Rus', Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria, Russian nobility, Russia, Boyars of Moldavia and Wallachia, Wallachia and ...
s, disgruntled by the ongoing civil war, tried to entice various neighbors, including the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, into intervening. Some of them looked to their own profits, trying to organize support for their own ascension to the Russian throne. Others looked to their western neighbor, the Commonwealth, and its attractive Golden Freedom
Golden Liberty ( la, Aurea Libertas; pl, Złota Wolność, lt, Auksinė laisvė), sometimes referred to as Golden Freedoms, Nobles' Democracy or Nobles' Commonwealth ( pl, Rzeczpospolita Szlachecka or ''Złota wolność szlachecka'') was a po ...
s, and together with some Polish politicians planned for some kind of union between those two states. Yet others tried to tie their fates with that of Sweden in what became known as the De la Gardie Campaign and the Ingrian War
The Ingrian War ( sv, Ingermanländska kriget) between the Swedish Empire and the Tsardom of Russia lasted between 1610 and 1617. It can be seen as part of Russia's Time of Troubles and is mainly remembered for the attempt to put a Swedish duke ...
.
Advocates for a union of Poland–Lithuania with Russia proposed a plan similar to the original Polish–Lithuanian Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin ( pl, Unia lubelska; lt, Liublino unija) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the pe ...
involving a common foreign policy and military; the right for nobility to choose the place where they would live and to buy landed estates; removal of barriers for trade and transit; introduction of a single currency; increased religious tolerance in Russia (especially the right to build churches of non-Orthodox faiths); and the sending of boyar children for education in more developed Polish academies (like the Jagiellonian University
The Jagiellonian University (Polish: ''Uniwersytet Jagielloński'', UJ) is a public research university in Kraków, Poland. Founded in 1364 by King Casimir III the Great, it is the oldest university in Poland and the 13th oldest university in ...
). However, this project never gained much support. Many boyars feared that the union with the predominantly Catholic Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania would endanger Russia's Orthodox traditions and opposed anything that threatened Russian culture, especially the policies aimed at curtailing the influence of the Orthodox Church, intermarriage and education in Polish schools that had already led to successful Polonization
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
of the Ruthenian lands under Polish control.
The Polish invasion (1605–1606)
 For most of the 17th century, Sigismund III was occupied with internal problems of his own, like the Nobles' Rebellion in the Commonwealth and the wars with Sweden and in Moldavia. However, the impostor
For most of the 17th century, Sigismund III was occupied with internal problems of his own, like the Nobles' Rebellion in the Commonwealth and the wars with Sweden and in Moldavia. However, the impostor False Dmitry I
False Dmitry I ( rus, Лжедмитрий I, Lzhedmitriy I) (or Pseudo-Demetrius I) reigned as the Tsar of Russia from 10 June 1605 until his death on 17 May 1606 under the name of Dmitriy Ivanovich ( rus, Дмитрий Иванович). A ...
appeared in Poland in 1603 and soon found enough support among powerful magnates such as Michał Wiśniowiecki
Michał Wiśniowiecki ( uk, Михайло Михайлович Вишневецький; died 1616) was a Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth szlachcic, prince at Wiśniowiec, magnate, son of Michał Wiśniowiecki, grandfather of future Polish– ...
, Lew, and Jan Piotr Sapieha
Jan Piotr Sapieha (English: ''John Peter Sapieha'', 1569–1611) was a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman, general, politician, diplomat, governor of Uświat county, member of the Parliament and a skilled commander of the Polish troops stationing in th ...
, who provided him with funds for a campaign against Godunov. Commonwealth magnates looked forward to material gains from the campaign and control over Russia through False Dmitriy. In addition, both Polish magnates and Russian boyars advanced plans for a union between the Commonwealth and Russia, similar to the one Lew Sapieha had discussed in 1600 (when the idea had been dismissed by Godunov). Finally, the proponents of Catholicism saw in Dmitry a tool to spread the influence of their Church eastwards, and after promises of a united Catholic dominated Russo-Polish entity waging a war on the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders ...
s also provided him with funds and education. Although Sigismund declined to support Dmitry officially with the full might of the Commonwealth, the Polish king was always happy to support pro-Catholic initiatives and provided him with the sum of 4,000 zlotys–enough for a few hundred soldiers. Nonetheless, some of Dmitriy's supporters, especially among those involved in the rebellion
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
, actively worked to have Dmitry replace Sigismund. In exchange, in June 1604 Dmitry promised the Commonwealth "half of Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest c ...
territory". Many were skeptical about the future of this endeavor. Jan Zamoyski
Jan Sariusz Zamoyski ( la, Ioannes Zamoyski de Zamoscie; 19 March 1542 – 3 June 1605) was a Polish nobleman, magnate, and the 1st '' ordynat'' of Zamość. He served as the Royal Secretary from 1565, Deputy Chancellor from 1576, Grand Cha ...
, opposed to most of Sigismund's policies, later referred to the entire False Dmitry I affair as a "comedy worthy of Plautus
Titus Maccius Plautus (; c. 254 – 184 BC), commonly known as Plautus, was a Roman playwright of the Old Latin period. His comedies are the earliest Latin literary works to have survived in their entirety. He wrote Palliata comoedia, the gen ...
or Terentius
The gens Terentia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Dionysius mentions a Gaius Terentius Arsa, tribune of the plebs in 462 BC, but Livy calls him ''Terentilius'', and from inscriptions this would seem to be a separate gens.Livy, iii. 9.Dio ...
".
When Boris Godunov
Borís Fyodorovich Godunóv (; russian: Борис Фёдорович Годунов; 1552 ) ruled the Tsardom of Russia as ''de facto'' regent from c. 1585 to 1598 and then as the first non-Rurikid tsar from 1598 to 1605. After the end of his ...
heard about the pretender, he claimed that the man was just a runaway monk called Grigory Otrepyev, although on what information he based this claim is unclear. Godunov's support among the Russians began to wane, especially when he tried to spread counter-rumors. Some of the Russian boyar
A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the Feudalism, feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Kievan Rus', Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria, Russian nobility, Russia, Boyars of Moldavia and Wallachia, Wallachia and ...
s also claimed to accept Dmitry as such support gave them legitimate reasons not to pay taxes to Godunov.
 Dmitry attracted a number of followers, formed a small army, and, supported by approximately 3500 soldiers of the Commonwealth magnates' private armies and the mercenaries bought by Dmitriy's own cash, rode to Russia in June 1604. Some of Godunov's other enemies, including approximately 2,000 southern
Dmitry attracted a number of followers, formed a small army, and, supported by approximately 3500 soldiers of the Commonwealth magnates' private armies and the mercenaries bought by Dmitriy's own cash, rode to Russia in June 1604. Some of Godunov's other enemies, including approximately 2,000 southern Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
s, joined Dimitry's forces on his way to Moscow. Dmitriy's forces fought two engagements with reluctant Russian soldiers; his army won the first at Novhorod-Siverskyi
Novhorod-Siverskyi ( uk, Новгород-Сіверський ) is a historic city in Chernihiv Oblast (province) of Ukraine. It is the administrative center of Novhorod-Siverskyi Raion, although until 18 July 2020 it was incorporated as a city ...
, soon capturing Chernigov
Chernihiv ( uk, Черні́гів, , russian: Черни́гов, ; pl, Czernihów, ; la, Czernihovia), is a List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in northern Ukraine, which serves as the administrative ...
, Putivl
Putyvl′Frank SysynBetween Poland and the Ukraine: The Dilemma of Adam Kysil, 1600-1653 - P. 25. (, ) or Putivl′ ( rus, Пути́вль, p=pʊˈtʲivlʲ) is a city in north-east Ukraine, in Sumy Oblast. The city served as the administrative c ...
, Sevsk Sevsk (russian: Севск) is the name of several inhabited localities in Russia.
;Urban localities
*Sevsk, Bryansk Oblast, a town in Sevsky District of Bryansk Oblast;
;Rural localities
* Sevsk, Kemerovo Oblast, a settlement in Burlakovskaya R ...
, and Kursk
Kursk ( rus, Курск, p=ˈkursk) is a city and the administrative center of Kursk Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Kur, Tuskar, and Seym rivers. The area around Kursk was the site of a turning point in the Soviet–German stru ...
, but badly lost the second Battle of Dobrynichi
The Battle of Dobrynichi took place on 21 January 1605 between the armies of False Dmitry I and ''Fyodor Mstislavsky'' near the village of Dobrynichi (today's Bryansk Oblast in Russia).
Prelude
Fyodor Mstislavsky commanded an army of some 20, ...
and nearly disintegrated. Dmitry's cause was only saved by the news of the death of Tsar Boris Godunov.
The sudden death of the Tsar on 13 April 1605 removed the main barrier to further advances by Dimitry. Russian troops began to defect to his side, and, on 1 June, boyars in Moscow imprisoned the newly crowned tsar, Boris's son Feodor II
Fyodor II Borisovich Godunov (russian: Фёдор II Борисович Годунов) (1589 – 20 June 1605) was tsar of Russia during the spring of 1605, at the beginning of the Time of Troubles.
Life
Fyodor II was born in Moscow, the son a ...
, and the boy's mother, later brutally murdering them. On 20 June the impostor made his triumphal entry into Moscow, and on 21 July he was crowned Tsar by a new Patriarch
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and in certai ...
of his own choosing, the Greek Cypriot
Greek Cypriots or Cypriot Greeks ( el, Ελληνοκύπριοι, Ellinokýprioi, tr, Kıbrıs Rumları) are the ethnic Greek population of Cyprus, forming the island's largest ethnolinguistic community. According to the 2011 census, 659,115 r ...
Patriarch Ignatius, who as bishop of Ryazan
Ryazan ( rus, Рязань, p=rʲɪˈzanʲ, a=ru-Ryazan.ogg) is the largest city and administrative center of Ryazan Oblast, Russia. The city is located on the banks of the Oka River in Central Russia, southeast of Moscow. As of the 2010 Census ...
had been the first church leader to recognize Dmitry as Tsar. The alliance with Poland was furthered by Dimitriy's marriage ('' per procura'' in Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
) with the daughter of Jerzy Mniszech
Jerzy Mniszech (c. 1548 – 1613) was a Poles, Polish Szlachta, nobleman and diplomat in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Member of the Mniszchowie, House of Mniszech. Krajczy koronny in 1574, castellan of Radom in 1583, voivode of Sandom ...
, Marina Mniszech
Marina Mniszech, ( pl, Maryna Mniszech; russian: Марина Мнишек, Marina Mnishek, ) also known in Russian lore as Marinka the Witch ( 1588 – 24 December 1614) was a Polish noblewoman who became the Tsaritsa of Russia during the Time ...
, a Polish noblewoman with whom Dmitry had fallen in love while in Poland. The new Tsarina outraged many Russians by refusing to convert from Catholicism to the Russian Orthodox faith. Commonwealth king Sigismund was a prominent guest at this wedding. Marina soon left to join her husband in Moscow, where she was crowned a Tsarina in May.
While Dmitry's rule itself was nondescript and devoid of significant blunders, his position was weak. Many boyars felt they could gain more influence, even the throne, for themselves, and many were still wary of Polish cultural influence, especially in view of Dmitriy's court being increasingly dominated by the aliens he brought with himself from Poland. The Golden Freedoms
Golden Liberty ( la, Aurea Libertas; pl, Złota Wolność, lt, Auksinė laisvė), sometimes referred to as Golden Freedoms, Nobles' Democracy or Nobles' Commonwealth ( pl, Rzeczpospolita Szlachecka or ''Złota wolność szlachecka'') was a pol ...
, declaring all nobility equal, that were supported by lesser nobility, threatened the most powerful of the boyars. Thus the boyars, headed by Prince Vasily Shuyski, began to plot against Dmitry and his pro-Polish faction, accusing him of homosexuality
Homosexuality is romantic attraction, sexual attraction, or sexual behavior between members of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" to peop ...
, spreading Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
and Polish customs, and selling Russia to Jesuits
The Society of Jesus ( la, Societas Iesu; abbreviation: SJ), also known as the Jesuits (; la, Iesuitæ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
and the Pope. They gained popular support, especially as Dmitry was visibly supported by a few hundred irregular Commonwealth forces, which still garrisoned Moscow, and often engaged in various criminal acts, angering the local population.
On the morning of 17 May 1606, about two weeks after the marriage, conspirators stormed the Kremlin
The Kremlin ( rus, Московский Кремль, r=Moskovskiy Kreml', p=ˈmɐˈskofskʲɪj krʲemlʲ, t=Moscow Kremlin) is a fortified complex in the center of Moscow founded by the Rurik dynasty. It is the best known of the kremlins (Ru ...
. Dmitry tried to flee through a window but broke his leg in the fall. One of the plotters shot him dead on the spot. At first, the body was put on display, but it was later cremated; the ashes were reportedly shot from a cannon toward Poland. Dmitriy's reign had lasted a mere ten months. Vasili Shuyski took his place as Tsar. About five hundred of Dmitriy's Commonwealth supporters were killed, imprisoned, or forced to leave Russia.
The Second Polish invasion (1607–1609)
 Tsar Vasili Shuyski was unpopular and weak in Russia and his reign was far from stable. He was perceived as anti-Polish; he had led the coup against the first False Dmitry, killing over 500 Polish soldiers in Moscow and imprisoning a Polish envoy. The civil war raged on, as in 1607 the False Dmitry II appeared, again supported by some Polish
Tsar Vasili Shuyski was unpopular and weak in Russia and his reign was far from stable. He was perceived as anti-Polish; he had led the coup against the first False Dmitry, killing over 500 Polish soldiers in Moscow and imprisoning a Polish envoy. The civil war raged on, as in 1607 the False Dmitry II appeared, again supported by some Polish magnate
The magnate term, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders, or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
s and 'recognized' by Marina Mniszech as her first husband. This brought him the support of the magnates of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who had supported False Dmitry I before. Adam Wiśniowiecki
Adam Wiśniowiecki (c. 1566 – 1622) Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth szlachcic and magnate. Supported False Dmitriy I during the Muscovy Time of Troubles, famous, together with Konstanty Wiśniowiecki (1564-1641), for being the 'finders' of ...
, Roman Różyński, Jan Piotr Sapieha
Jan Piotr Sapieha (English: ''John Peter Sapieha'', 1569–1611) was a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman, general, politician, diplomat, governor of Uświat county, member of the Parliament and a skilled commander of the Polish troops stationing in th ...
decided to support the second pretender as well, supplying him with some early funds and about 7,500 soldiers. The pillaging of his army, especially of the Lisowczycy
Lisowczyks or Lisowczycy (; also known as ''Straceńcy'' ('lost men' or 'forlorn hope') or (company of ); or in singular form: Lisowczyk or ) was the name of an early 17th-century irregular unit of the Polish–Lithuanian light cavalry. The Lis ...
mercenaries
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any o ...
led by Aleksander Lisowski, contributed to the placard in Sergiyev Posad
Sergiyev Posad ( rus, Се́ргиев Поса́д, p=ˈsʲɛrgʲɪ(j)ɪf pɐˈsat) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Sergiyevo-Posadsky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia. Population:
It was pre ...
: "three plagues: typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposure.
...
, Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
and Poles". In 1608 together with Aleksander Kleczkowski, Lisowczycy, leading a few hundred in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Don Cossack
Don Cossacks (russian: Донские казаки, Donskie kazaki) or Donians (russian: донцы, dontsy) are Cossacks who settled along the middle and lower Don. Historically, they lived within the former Don Cossack Host (russian: До� ...
s working for the Commonwealth, ragtag szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in the ...
and mercenaries, defeated the army of tsar Vasili Shuyski led by Zakhary Lyapunov
Zakhary Petrovich Lyapunov () (? - after 1612) was a Russian political figure of the early 17th century, brother of Prokopy Lyapunov.
Biography
In 1605, Zakhary Lyapunov took the side of False Dmitri I. Upon the latter's death in 1606, he took ...
and Ivan Khovansky at the Battle of Zaraysk and captured Mikhailov and Kolomna
Kolomna ( rus, Колóмна, p=kɐˈlomnə) is a historical types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, situated at the confluence of the Moskva River, Moskva and Oka Rivers, (by rail) southeast of Moscow. Populati ...
. Then Lisowczycy advanced towards Moscow but was defeated by Vasiliy Buturlin
Vasiliy Vasilyevich Buturlin (Died 1656) was a noble ( boyar) Muscovite military leader and diplomat. He is better known for serving as a Muscovite envoy during negotiations with Bohdan Khmelnytskyi in Pereyaslav in 1654. Next year Buturlin success ...
at the Battle of Medvezhiy Brod, losing most of his plunder. When Polish commander Jan Piotr Sapieha
Jan Piotr Sapieha (English: ''John Peter Sapieha'', 1569–1611) was a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman, general, politician, diplomat, governor of Uświat county, member of the Parliament and a skilled commander of the Polish troops stationing in th ...
failed to win the siege of Troitse-Sergiyeva Lavra
The siege of the Troitsky monastery (''Троицкая осада'', ''Троицкое сидение'' in Russian, Siege of Saint Trinity) was an abortive attempt of the Polish–Lithuanian irregular army that acted in support of False Dmitry ...
, Lisowczycy retreated to the vicinity of Rakhmantsevo. Soon, however, came successes (pillages) at Kostroma
Kostroma ( rus, Кострома́, p=kəstrɐˈma) is a historic city and the administrative center of Kostroma Oblast, Russia. A part of the Golden Ring of Russian cities, it is located at the confluence of the rivers Volga and Kostroma. Popu ...
, Soligalich
Soligalich (russian: Солига́лич) is a town and the administrative center of Soligalichsky District in Kostroma Oblast, Russia, located on the right bank of the Kostroma River. Population:
History
It originated as an important center ...
, and some other cities.
Dmitry speedily captured Karachev
Karachev (russian: Карачев) is an ancient town and the administrative center of Karachevsky District in Bryansk Oblast, Russia. Population:
History
First chronicled in 1146, it was the capital of one of the Upper Oka Principalities in t ...
, Bryansk
Bryansk ( rus, Брянск, p=brʲansk) is a city and the administrative center of Bryansk Oblast, Russia, situated on the River Desna, southwest of Moscow. Population:
Geography Urban layout
The location of the settlement was originally ass ...
, and other towns. He was reinforced by the Poles, and in the spring of 1608 advanced upon Moscow, routing the army of Tsar Vasily Shuyski at Bolkhov
Bolkhov (russian: Бо́лхов) is a town and the administrative center of Bolkhovsky District in Oryol Oblast, Russia, located on the Nugr River (Oka's tributary), from Oryol, the administrative center of the oblast. Population: 12,800 (1 ...
. Dmitry's promises of the wholesale confiscation of the estates of the boyars drew many common people to his side. The village of Tushino
Tushino ( rus, Тушино, p=ˈtuʂɨnə) is a former village and town to the north of Moscow, which has been part of the city's area since 1960. Between 1939 and 1960, Tushino was classed as a separate town. The Skhodnya River flows across the ...
, about twelve kilometers from the capital, was converted into an armed camp, where Dmitry gathered his army. His forces initially included 7,000 Polish soldiers, 10,000 Cossacks, and 10,000 other soldiers, including former members of the failed rokosz of Zebrzydowski, but his force grew gradually in power, and soon exceeded 100,000 men. He raised another illustrious captive, Feodor Romanov
Feodor Nikitich Romanov (russian: Фео́дор Ники́тич Рома́нов, ; 1553 – 1 October 1633) was a Russian boyar who after temporary disgrace rose to become patriarch of Moscow as Filaret (russian: Филаре́т, ), and bec ...
, to the rank of Patriarch
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and in certai ...
, enthroning him as Patriarch Filaret, and won the allegiance of the cities of Yaroslavl
Yaroslavl ( rus, Ярослáвль, p=jɪrɐˈsɫavlʲ) is a city and the administrative center of Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, located northeast of Moscow. The historic part of the city is a World Heritage Site, and is located at the confluence ...
, Kostroma
Kostroma ( rus, Кострома́, p=kəstrɐˈma) is a historic city and the administrative center of Kostroma Oblast, Russia. A part of the Golden Ring of Russian cities, it is located at the confluence of the rivers Volga and Kostroma. Popu ...
, Vologda
Vologda ( rus, Вологда, p=ˈvoləɡdə) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Vologda Oblast, Russia, located on the river Vologda (river), Vologda within the watershed of the Northern Dvina. ...
, Kashin, and several others. However, his fortunes were soon to reverse, as the Commonwealth decided to take a more active stance in the Russian civil wars.
Polish–Muscovite War (1609–1618)
Polish victories (1609–1610)
 In 1609 the Zebrzydowski Rebellion ended when Tsar Vasili signed a military alliance with
In 1609 the Zebrzydowski Rebellion ended when Tsar Vasili signed a military alliance with Charles IX of Sweden
Charles IX, also Carl ( sv, Karl IX; 4 October 1550 – 30 October 1611), reigned as King of Sweden from 1604 until his death. He was the youngest son of King Gustav I () and of his second wife, Margaret Leijonhufvud, the brother of King Eric X ...
(on 28 February 1609). The Commonwealth king Sigismund III, whose primary goal was to regain the Swedish throne, got permission from the Polish Sejm (Parliament) to declare war
A declaration of war is a formal act by which one state announces existing or impending war activity against another. The declaration is a performative speech act (or the signing of a document) by an authorized party of a national government, in ...
on Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
. He viewed it as an excellent opportunity to expand the Commonwealth's territory and sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal al ...
, with hopes that the eventual outcome of the war would Catholicize Orthodox
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to:
Religion
* Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-pa ...
Russia (in this he was strongly supported by the Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
) and enable him to defeat Sweden. This plan also allowed him to give a purpose to the numerous restless former supporters of Zebrzydowski, luring them with promises of wealth and fame awaiting members of the campaign beyond the Commonwealth's eastern border. A book published that year by the well-travelled Polish Silesian nobleman, courtier
A courtier () is a person who attends the royal court of a monarch or other royalty. The earliest historical examples of courtiers were part of the retinues of rulers. Historically the court was the centre of government as well as the official r ...
and political activist Paweł Palczowski of Palczowic, ''Kolęda moskiewska'' (''The Muscovite Carol''), compared Russia to the Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
empires of the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
, full of golden cities and easy to conquer. The treatise
A treatise is a formal and systematic written discourse on some subject, generally longer and treating it in greater depth than an essay, and more concerned with investigating or exposing the principles of the subject and its conclusions."Treat ...
was written to promote Polish colonialism and persuade delegates of the Sejm in January 1609 to support Sigismund III's expedition to Muscovy Muscovy is an alternative name for the Grand Duchy of Moscow (1263–1547) and the Tsardom of Russia (1547–1721). It may also refer to:
*Muscovy Company, an English trading company chartered in 1555
* Muscovy duck (''Cairina moschata'') and Domes ...
. Palczowski himself participated in and perished during Sigismund's Muscovy expedition.Sarmatian Review, Rice University, Texas, January 2011, Vol. XXXI, No. 1., p. 1561; ''The Muscovite Carol (Kolęda moskiewska)'' by Paweł Palczowski of Palczowic. Edited by Grzegorz Franczak/ref> Some Russian boyars assured Sigismund of their support by offering the throne to his son, Prince Wladislaus IV of Poland, Władysław. Previously, Sigismund had been unwilling to commit the majority of Polish forces or his time to the internal conflict in Russia, but in 1609 those factors made him re-evaluate and drastically change his policy. Although many Polish nobles and soldiers were fighting for the second False Dmitry at the time, Sigismund III and the troops under his command did not support Dimitriy for the throne – Sigismund wanted Russia himself. The entry of Sigismund into Russia caused the majority of the Polish supporters of False Dmitry II to desert him and contributed to his defeat. A series of subsequent disasters induced False Dmitry II to flee his camp disguised as a peasant and to go to Kostroma together with Marina. Dmitry made another unsuccessful attack on Moscow, and, supported by the
Don Cossacks
Don Cossacks (russian: Донские казаки, Donskie kazaki) or Donians (russian: донцы, dontsy) are Cossacks who settled along the middle and lower Don. Historically, they lived within the former Don Cossack Host (russian: До� ...
, recovered a hold over all of south-eastern Russia. He was killed, however, while half drunk, on 11 December 1610 by a Qasim Tatar princeling Pyotr Urusov, whom Dimitriy had flogged on a previous occasion.
A Commonwealth army under the command of Hetman
( uk, гетьман, translit=het'man) is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders.
Used by the Czechs in Bohemia since the 15th century. It was the title of the second-highest military co ...
Stanisław Żółkiewski
Stanisław Żółkiewski (; 1547 – 7 October 1620) was a Polish nobleman of the Lubicz coat of arms, magnate, military commander and a chancellor of the Polish crown of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, who took part in many campaigns of ...
, who was generally opposed to this conflict but could not disobey the king's orders, crossed the border and on 29 September 1609 laid siege to Smolensk, an important city Russia had captured from Lithuania in 1514. Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest c ...
was manned by fewer than 1,000 Russian men commanded by the voivod Mikhail Shein
Mikhail Borisovich Shein (Михаил Борисович Шеин, ) (late 1570s–1634) was a leading Russian general during the reign of Tsar Mikhail Romanov. Despite his tactical skills and successful military career, he ended up losing his ar ...
, while Żółkiewski commanded 12,000 troops. However, Smolensk had one major advantage: the previous Tsar, Boris Godunov, had sponsored the fortification of the city with a massive fortress completed in 1602. The Poles found it impenetrable; they settled into a long siege, firing artillery into the city, attempting to tunnel under the moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
, and building earthen rampart
Rampart may refer to:
* Rampart (fortification), a defensive wall or bank around a castle, fort or settlement
Rampart may also refer to:
* "O'er the Ramparts We Watched" is a key line from "The Star-Spangled Banner", the national anthem of the ...
s, remnants of which can still be seen today. The siege lasted 20 months before the Poles with the help of a Russian defector named Andrei Dedishin eventually succeeded in taking the fortress.
Jan Karol Chodkiewicz
Jan Karol Chodkiewicz ( lt, Jonas Karolis Chodkevičius, be, Ян Караль Хадкевіч ; 1561 – 24 September 1621) was a military commander of the Grand Ducal Lithuanian Army, who was from 1601 Field Hetman of Lithuania, and from ...
with 2,000 men, ended in defeat when the unpaid Commonwealth army mutinied and compelled their leader to retreat through the heart of Russia and back to Smolensk. Not until Crown Prince Władysław, arrived with tardy reinforcements did the war assume a different character. In the meantime, Lisowczycy took and plundered Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=pskov-ru.ogg, p=pskof; see also names in other languages) is a city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, located about east of the Estonian border, on the Velikaya River. Population ...
in 1610 and clashed with the Swedes operating in Russia during the Ingrian War
The Ingrian War ( sv, Ingermanländska kriget) between the Swedish Empire and the Tsardom of Russia lasted between 1610 and 1617. It can be seen as part of Russia's Time of Troubles and is mainly remembered for the attempt to put a Swedish duke ...
.
Several different visions of the campaign and political goals clashed in the Polish camp. Some of the former members of the Zebrzydowski Rebellion, opponents of Sigismund, actually advanced proposals to have Sigismund dethroned and Dmitriy, or even Shuyski, elected king. Żółkiewski, who from the beginning opposed the invasion of Russia, came into conflict with Sigismund over the scope, methods, and goal of the campaign. Żółkiewski represented the traditional views of Polish nobility, the szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in the ...
, which did not support waging aggressive and dangerous wars against a strong enemy like Russia. Thus Żółkiewski favored the plans for peaceful and voluntary union, much like that with Lithuania. Żółkiewski offered Russian boyars rights and religious freedom, envisioning an association resulting in the creation of the Polish–Lithuanian–Muscovite Commonwealth. To that end, he felt that Moscow's cooperation should be gained via diplomacy, not force. Sigismund III, however, did not want to engage in political deals and compromises, especially when these had to include concessions to the Orthodox Church. Sigismund was a vocal, almost fanatical, supporter of the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and counter-reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
, and believed that he could win everything and take Moscow by force, and then establish his own rule along with the rule of Roman Catholicism.
Poles in Moscow (1610)
On 31 January 1610 Sigismund received a delegation of boyars opposed to Shuyski, who asked Władysław to become the tsar. On 24 February Sigismund sent them a letter in which he agreed to do so, but only when Moscow was at peace.battle of Klushino
The Battle of Klushino, or the Battle of Kłuszyn, was fought on 4 July 1610, between forces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia during the Polish–Muscovite War, part of Russia's Time of Troubles. The battle occ ...
(Kłuszyn), where 7,000 Polish elite cavalry, the winged hussars, led by the hetman himself, defeated the numerically superior Russian army of about 35,000–40,000 soldiers. This giant and surprising defeat of the Russians shocked everyone and opened a new phase in the conflict.
 After the news of Klushino spread, support for Tsar Shuyski almost completely evaporated. Żółkiewski soon convinced the Russian units at Tsaryovo, which were much stronger than the ones at Kłuszyn, to capitulate and to swear an oath of loyalty to Władysław. Then he incorporated them into his army and moved towards Moscow. In August 1610 many Russian
After the news of Klushino spread, support for Tsar Shuyski almost completely evaporated. Żółkiewski soon convinced the Russian units at Tsaryovo, which were much stronger than the ones at Kłuszyn, to capitulate and to swear an oath of loyalty to Władysław. Then he incorporated them into his army and moved towards Moscow. In August 1610 many Russian boyar
A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the Feudalism, feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Kievan Rus', Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria, Russian nobility, Russia, Boyars of Moldavia and Wallachia, Wallachia and ...
s accepted that Sigismund III was victorious and that Władysław would become the next tsar if he converted to Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first m ...
. The Russian Duma
A duma (russian: дума) is a Russian assembly with advisory or legislative functions.
The term ''boyar duma'' is used to refer to advisory councils in Russia from the 10th to 17th centuries. Starting in the 18th century, city dumas were for ...
voted for Tsar Shuyski to be removed from the throne. Shuyski's family, including the tsar, were captured, and Shuyski was reportedly taken to a monastery, forcibly shaved as a monk, and compelled to remain at the monastery under guard. He was later sent to Warsaw, as a kind of war trophy, and eventually died in Gostynin
Gostynin is a town in central Poland with 19,414 inhabitants (2004). It is situated in the Masovian Voivodship since 1999 and was previously in the Płock Voivodship from 1975 to 1998. It is the capital of Gostynin County.
History
Gostynin h ...
.
Shortly after Shuyski was removed, both Żółkiewski and the second False Dmitri arrived at Moscow with their separate armies. It was a tense moment, filled with the confusion of the conflict. Various pro- and anti-Polish, Swedish, and domestic boyar factions vied for temporary control of the situation. The Russian army and the people themselves were unsure if this was an invasion and that they should close and defend the city, or if it was a liberating force that should be allowed in and welcomed as allies. After a few skirmishes, the pro-Polish faction gained dominance, and the Poles were allowed into Moscow on 8 October. The boyars opened Moscow's gates to the Polish troops and asked Żółkiewski to protect them from anarchy. The Moscow Kremlin
The Kremlin ( rus, Московский Кремль, r=Moskovskiy Kreml', p=ˈmɐˈskofskʲɪj krʲemlʲ, t=Moscow Kremlin) is a fortified complex in the center of Moscow founded by the Rurik dynasty. It is the best known of the kremlins (R ...
was then garrisoned by Polish troops commanded by Aleksander Gosiewski
Aleksander Korwin Gosiewski ( lt, Aleksandras Korvinas Gosievskis) ''de armis'' Ślepowron (b. – d. 1639), was a Polish nobleman, military commander and diplomat, Lithuanian Field-Quartermaster since 1630, Palatine-Governor of Smolensk fr ...
. On 27 July a treaty was signed between the boyars and Żółkiewski promising the Russian boyars the same vast privileges the Polish Szlachta had, in exchange for them recognizing Władysław as the new tsar. However, Żółkiewski did not know that Sigismund, who remained at Smolensk, already had other plans.
 In the meantime, Żółkiewski and the second False Dmitriy, formerly reluctant allies, began to part ways. The second False Dmitry had lost much of his influence over the Polish court, and Żółkiewski would eventually try to drive Dmitry from the capital. Żółkiewski soon began manoeuvring for a tsar of Polish origin, particularly the 15-year-old Prince Władysław. The boyars had offered the throne to Władysław at least twice, in the hopes of having the
In the meantime, Żółkiewski and the second False Dmitriy, formerly reluctant allies, began to part ways. The second False Dmitry had lost much of his influence over the Polish court, and Żółkiewski would eventually try to drive Dmitry from the capital. Żółkiewski soon began manoeuvring for a tsar of Polish origin, particularly the 15-year-old Prince Władysław. The boyars had offered the throne to Władysław at least twice, in the hopes of having the liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth end the despotic
Despotism ( el, Δεσποτισμός, ''despotismós'') is a form of government in which a single entity rules with absolute power. Normally, that entity is an individual, the despot; but (as in an autocracy) societies which limit respect an ...
rule of their current tsars. Through Żółkiewski's work, the pro-Polish factions among the boyars (composed of knyazes Fyodor Mstislavsky, Vasily Galitzine
Prince Vasily Vasilyevich Golitsyn (russian: Василий Васильевич Голицын, tr. ; 1643–1714) was a Russian aristocrat and statesman of the 17th century. He belonged to the Golitsyn as well as Romodanovsky Muscovite noble ...
, Fyodor Sheremetev, Daniil Mezetsky and diaks Vasily Telepnyov, and Tomiło Łagowski) gained dominance and once again a majority of the boyars said that they would support Władysław for the throne, if he converted to Orthodoxy and if the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth returned the fortresses that they had captured in the war.
However, Sigismund, supported by some of the more devout and zealous nobility, was completely opposed to the conversion of the prince. From that point the planned Polish–Lithuanian–Muscovite union began to fall apart. Offended and angered by Sigismund, the boyars dragged their feet on supporting Władysław. They were divided between electing Vasily Galitzine
Prince Vasily Vasilyevich Golitsyn (russian: Василий Васильевич Голицын, tr. ; 1643–1714) was a Russian aristocrat and statesman of the 17th century. He belonged to the Golitsyn as well as Romodanovsky Muscovite noble ...
, Michael Romanov (also 15 years old), or the second False Dmitriy. Żółkiewski acted quickly, making promises without the consent of the still-absent king, and the boyars elected Władysław as the new tsar. Żółkiewski had the most prominent of the opponents, Fyodor Romanov
Feodor Nikitich Romanov (russian: Фео́дор Ники́тич Рома́нов, ; 1553 – 1 October 1633) was a Russian boyar who after temporary disgrace rose to become patriarch of Moscow as Filaret (russian: Филаре́т, ), and bec ...
, Michael's father and the patriarch of Moscow
The Patriarch of Moscow and all Rus' (russian: Патриарх Московский и всея Руси, translit=Patriarkh Moskovskij i vseja Rusi), also known as the Patriarch of Moscow and all Russia, is the official title of the Bishop of Mo ...
, exiled from Russia in order to secure Polish support. After the election of Władysław, the second False Dmitry fled from Tushino
Tushino ( rus, Тушино, p=ˈtuʂɨnə) is a former village and town to the north of Moscow, which has been part of the city's area since 1960. Between 1939 and 1960, Tushino was classed as a separate town. The Skhodnya River flows across the ...
, a city near Moscow, to his base at Kaluga
Kaluga ( rus, Калу́га, p=kɐˈɫuɡə), a city and the administrative center of Kaluga Oblast in Russia, stands on the Oka River southwest of Moscow. Population:
Kaluga's most famous resident, the space travel pioneer Konstantin Tsiol ...
. However, his position was precarious even there, and he was killed on 20 December by one of his own men. Marina Mniszech, though, was pregnant with the new "heir" to the Russian throne, Ivan Dmitriyevich, and she would still be a factor in Russian politics until her eventual death in 1614.
Władysław faced further opposition from a seemingly unlikely party: his father. When Żółkiewski returned to meet Sigismund at Smolensk in November of that year, Sigismund III changed his mind and decided that he could gain the Russian throne for himself. A majority of the Russians opposed the move, especially as Sigismund didn't hide his intent to Catholicize and Polonize the Russian Tsardom. Żółkiewski found himself in an awkward position – he had promised the boyars Prince Władysław to keep the Russian throne for Poland, and he knew that they would not accept Sigismund III, who was unpopular throughout Russia. However, he also had to explain this to his king, who was convinced, from his conquests in the west, of his popularity in Russia. Eventually, Żółkiewski, disappointed with Sigismund, returned to Poland. Sigismund eventually compromised and decided that he would allow his son to take the throne and that he would rule as regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
until Władysław came of age. Thus, he required that the boyars who submitted and swore allegiance to Prince Władysław would also have to swear an oath to him. The boyars were more resistant to this request and support for the Poles eroded fast. Władysław was never able to take real power, and the war soon resumed. Sigismund and Władysław left the city for safer ground as tensions grew, and the small Polish garrison at the Kremlin soon became isolated and subject to increased hostility, as more and more of the formerly pro-Polish boyars began to change factions. The Polish forces outside Moscow under the command of Jan Piotr Sapieha
Jan Piotr Sapieha (English: ''John Peter Sapieha'', 1569–1611) was a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman, general, politician, diplomat, governor of Uświat county, member of the Parliament and a skilled commander of the Polish troops stationing in th ...
clashed with the growing anti-Polish Russian forces of the so-called First Volunteer Army, led by Prokopy Lyapunov
Prokopy Petrovich Lyapunov () (Isady, Grand Duchy of Moscow; Grand Duchy of Ryazan became a part of Grand Duchy of Moscow in 1521 and Moscow shouldn't be confused as a birth place which is located to the east of Old Ryazan, in a village that sur ...
.
In the meantime, the siege of Smolensk continued, even as Władysław was named tsar of Russia and cities and forts throughout the area swore allegiance to the Poles. However, Sigismund III required that Smolensk not only swear allegiance, but open its gates to the Poles, which the Russians refused to do. Żółkiewski fortified Moscow with his army and returned to King Sigismund III, who had remained at Smolensk while Żółkiewski negotiated in Moscow. The largest tunneling project at Smolensk came in December 1610; however, the Poles only managed to destroy more of the outer wall – the inner wall remained intact. The siege continued. At one point, the Polish guns breached the outer wall, and the governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
of Braclaw
Bratslav ( uk, Брацлав; pl, Bracław; yi, בראָצלעוו, ''Brotslev'', today also pronounced Breslev or '' Breslov'' as the name of a Hasidic group, which originated from this town) is an urban-type settlement in Ukraine, located ...
(Bracław) ordered his soldiers to rush in; however, the Russians had predicted where the breach would occur and had fortified that part of the wall with additional men. Both sets of troops were slaughtered, and the Poles were eventually beaten back.
The war resumes (1611)
 A 1611 uprising in Moscow against the Polish garrison marked the end of Russian tolerance for the Commonwealth intervention. The citizens of Moscow had voluntarily participated in the coup in 1606, killing 500 Polish soldiers. Now, ruled by the Poles, they once again revolted. The Moscow burghers took over the munition store, but Polish troops defeated the first wave of attackers, and the fighting resulted in a large fire that consumed part of Moscow. From July onward the situation of the Commonwealth forces became grave, as the uprising turned into a siege of the Polish-held Kremlin. Reportedly, the Poles had imprisoned the leader of the Orthodox Church,
A 1611 uprising in Moscow against the Polish garrison marked the end of Russian tolerance for the Commonwealth intervention. The citizens of Moscow had voluntarily participated in the coup in 1606, killing 500 Polish soldiers. Now, ruled by the Poles, they once again revolted. The Moscow burghers took over the munition store, but Polish troops defeated the first wave of attackers, and the fighting resulted in a large fire that consumed part of Moscow. From July onward the situation of the Commonwealth forces became grave, as the uprising turned into a siege of the Polish-held Kremlin. Reportedly, the Poles had imprisoned the leader of the Orthodox Church, Patriarch Hermogenes
Hermogenes, or Germogen (russian: Гермоге́н) (secular name Yermolay) (before 1530 – 17 February 1612) was the Patriarch of Moscow and all Russia from 1606. It was he who inspired the popular uprising that put an end to the Time of Troub ...
. When the Russians attacked Moscow, the Poles ordered him, as the man with the most authority with the Russians at the time, to sign a statement to call off the attack. Hermogenes refused and was starved to death. The Polish Kremlin garrison then found itself besieged.
In the meantime, in late 1611, prince Dmitry Pozharsky
Dmitry Mikhaylovich Pozharsky ( rus, Дми́трий Миха́йлович Пожа́рский, p=ˈdmʲitrʲɪj mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪtɕ pɐˈʐarskʲɪj; 17 October 1577 – 30 April 1642) was a Russian prince known for his military leadershi ...
was asked to lead the public opposition against the Poles, organized by the merchants' guild of Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod ( ; rus, links=no, Нижний Новгород, a=Ru-Nizhny Novgorod.ogg, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪj ˈnovɡərət ), colloquially shortened to Nizhny, from the 13th to the 17th century Novgorod of the Lower Land, formerly known as Gork ...
. The respected town butcher (literally, a meat-trader) Kuzma Minin
Kuzma (Kozma) Minin (; full name Kuzma Minich Zakhariev-Sukhoruky, born late 1570s - died 1616) was a Russian merchant from Nizhny Novgorod, Russia, who, together with Prince Dmitry Pozharsky, became a national hero for his role in defending the ...
oversaw the handling of funds donated by the merchants to form the Second Volunteer Army (russian: Второе народное ополчение). When part of the Polish army mutinied in January 1612 due to unpaid wages and retreated from Russia towards the Commonwealth, the forces of the Second Volunteer Army strengthened the other anti-Polish Russian forces in Moscow. The 9,000-strong Polish army under hetman
( uk, гетьман, translit=het'man) is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders.
Used by the Czechs in Bohemia since the 15th century. It was the title of the second-highest military co ...
Jan Karol Chodkiewicz
Jan Karol Chodkiewicz ( lt, Jonas Karolis Chodkevičius, be, Ян Караль Хадкевіч ; 1561 – 24 September 1621) was a military commander of the Grand Ducal Lithuanian Army, who was from 1601 Field Hetman of Lithuania, and from ...
attempted to lift the siege and clashed with Russian forces, attempting to break through to Polish forces in the Kremlin on 1 September. The Polish forces used cavalry attacks in the open field, exercising tactics that were new to them: escorting a mobile tabor
Tabor may refer to:
Places
Czech Republic
* Tábor, a town in the South Bohemian Region
** Tábor District, the surrounding district
* Tábor, a village and part of Velké Heraltice in the Moravian-Silesian Region
Israel
* Mount Tabor, Galilee ...
fortress through the city. After early Polish successes, the Russian Cossack reinforcements had forced Chodkiewicz's forces to retreat from Moscow.
 Russian reinforcements under Prince Pozharsky eventually starved the Commonwealth garrison (there were reports of
Russian reinforcements under Prince Pozharsky eventually starved the Commonwealth garrison (there were reports of cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
) and forced its surrender on 1 November (though some sources give 6 November or 7 November) after the 19-month siege. A historian (Parker) writes vividly of the Polish soldiers: "First they ate grass and offal, then they ate each other, and the survivors finally surrendered. The Moscow Kremlin fell on 6 November 1612." On 7 November, the Polish soldiers withdrew from Moscow. Although the Commonwealth negotiated a safe passage, the Russian forces massacred half of the former Kremlin garrison forces as they left the fortress.Tucker, S.C., Editor, 2010, ''A Global Chronology of Conflict'', Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO, LLC, Thus, the Russian army recaptured Moscow.
 On 2 June 1611 Smolensk had finally fallen to the Poles. After enduring 20 months of siege, two harsh winters and dwindling food supplies, the Russians in Smolensk finally reached their limit as the Polish–Lithuanian troops broke through the city gates. The Polish army, advised by the runaway traitor Andrei Dedishin, discovered a weakness in the fortress defenses, and on 13 June 1611 Cavalier of Malta Bartłomiej Nowodworski inserted a mine into a sewer canal. The explosion created a large breach in the fortress walls. The fortress fell on the same day. The remaining 3,000 Russian defenders took refuge in the Assumption Cathedral and blew themselves up with stores of gunpowder to avoid death at the hands of the invaders. Although it was a blow to lose Smolensk, the defeat freed up Russian troops to fight the Commonwealth in Moscow, and the Russian commander at Smolensk, Mikhail Borisovich Shein, was considered a hero for holding out as long as he had. He was captured at Smolensk and remained a prisoner of Poland–Lithuania for the next nine years.
On 2 June 1611 Smolensk had finally fallen to the Poles. After enduring 20 months of siege, two harsh winters and dwindling food supplies, the Russians in Smolensk finally reached their limit as the Polish–Lithuanian troops broke through the city gates. The Polish army, advised by the runaway traitor Andrei Dedishin, discovered a weakness in the fortress defenses, and on 13 June 1611 Cavalier of Malta Bartłomiej Nowodworski inserted a mine into a sewer canal. The explosion created a large breach in the fortress walls. The fortress fell on the same day. The remaining 3,000 Russian defenders took refuge in the Assumption Cathedral and blew themselves up with stores of gunpowder to avoid death at the hands of the invaders. Although it was a blow to lose Smolensk, the defeat freed up Russian troops to fight the Commonwealth in Moscow, and the Russian commander at Smolensk, Mikhail Borisovich Shein, was considered a hero for holding out as long as he had. He was captured at Smolensk and remained a prisoner of Poland–Lithuania for the next nine years.
A new respite (1612–1617)
 After the fall of Smolensk, the Russo-Polish border remained relatively quiet for the next few years. However, no official treaty was signed. Sigismund, criticized by the
After the fall of Smolensk, the Russo-Polish border remained relatively quiet for the next few years. However, no official treaty was signed. Sigismund, criticized by the Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland (Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of t ...
(the Polish parliament made up of the ''szlachta'', who were always reluctant to levy taxes upon themselves to pay for any military force) for his failure to keep Moscow, received little funding for the army. This led to a mutiny
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military, of a crew or of a crew of pirates) to oppose, change, or overthrow an organization to which they were previously loyal. The term is commonly used for a rebellion among member ...
of the Polish regular army (wojsko kwarciane
''Wojsko kwarciane'' (, ''quarter army'') was the term used for regular army units of Poland (Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth). The term was used since 1562.
''Wojsko kwarciane'' was formed from earlier '' obrona potoczna'' units.
The term "quar ...
), or rather to the specific semi-legal form of mutiny practiced in the Commonwealth: a konfederacja (''confederatio''). The resulting konfederacja rohaczewska was considered the largest and most vicious of the soldiers' konfederacja's in the history of the Commonwealth, and it pillaged Commonwealth territories from 1612 until the most rebellious of the konfederacja's were defeated on 17 May 1614 at the Battle of Rohatyn, whereupon the rest received their wages. The leader of the konfederacja, Jan Karwacki, was captured and sent in chains by the future hetman Stanisław Koniecpolski
Stanisław Koniecpolski (1591 – 11 March 1646) was a Polish military commander, regarded as one of the most talented and capable in the History of Poland in the Early Modern era (1569–1795), history of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. ...
to his mentor, hetman Żółkiewski, and later executed in Lwów
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukraine ...
. The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
further criticized Sigismund because the Cossacks in Ukraine once again had begun to make unsanctioned raids into Turkish territory. Thus, Poland–Lithuania got no support from the Ottoman Empire in its war.
In the meantime, the Russian Time of Troubles was far from over, and Russia had no strength to take advantage of the Commonwealth's weakness. On 21 February 1613 the Zemsky Sobor
The Zemsky Sobor ( rus, зе́мский собо́р, p=ˈzʲemskʲɪj sɐˈbor, t=assembly of the land) was a parliament of the Tsardom of Russia's estates of the realm active during the 16th and 17th centuries.
The assembly represented Russi ...
("assembly of the land") named Michael Romanov, the now 16-year-old son of Fyodor Romanov, the new tsar. Fyodor, now installed as Patriarch Filaret, was a popular boyar and patriarch of Moscow, one of several boyars who vied to gain control of the Russian throne during the Time of Troubles. The Romanovs were a powerful boyar family; Michael's great-aunt (the sister of his grandfather) was Anastasia Romanovna
Anastasia Romanovna Zakharyina-Yurieva (1530 – 7 August 1560) was the first spouse of the Russian Tsar Ivan the Terrible and the first Russian Tsaritsa. She was the mother of Feodor I, the last lineal Rurikid Tsar of Russia and the great-a ...
, the wife of Ivan the Terrible. However, the new tsar had many opponents. Marina Mniszech tried until her death in 1614 to install her child as Tsar of Russia; various boyar factions still vied for power, trying to unseat the young Tsar Michael; and Sweden intervened in force, trying to gain the throne for Duke Carl Philip, even succeeding for a few months. However, Philip received even less support than Władysław, and the Swedes were soon forced to retreat from Russia.
 While both countries were shaken by internal strife, many smaller factions thrived. Polish
While both countries were shaken by internal strife, many smaller factions thrived. Polish Lisowczycy
Lisowczyks or Lisowczycy (; also known as ''Straceńcy'' ('lost men' or 'forlorn hope') or (company of ); or in singular form: Lisowczyk or ) was the name of an early 17th-century irregular unit of the Polish–Lithuanian light cavalry. The Lis ...
mercenaries, who were essential in the defense of Smolensk in 1612, when most regulars (wojsko kwarciane) mutinied and joined the ''konfederacja rohatynska'', were content to guard the Polish border against the Russian incursions for the next three years. However, in 1615 Aleksander Józef Lisowski
Aleksander Józef Lisowski HNG (c. 1580 – October 11, 1616) was a Polish–Lithuanian noble ( szlachcic), commander of a mercenary group that after his death adopted the name "''Lisowczycy''." His coat of arms was ''Jeż'' (Hedgehog).
...
gathered many outlaws and invaded Russia with 6 '' chorągiew'' of cavalry. He besieged Bryansk
Bryansk ( rus, Брянск, p=brʲansk) is a city and the administrative center of Bryansk Oblast, Russia, situated on the River Desna, southwest of Moscow. Population:
Geography Urban layout
The location of the settlement was originally ass ...
and defeated the relief force of a few thousand soldiers under Prince Yuri Shakhovskoy near Karachev
Karachev (russian: Карачев) is an ancient town and the administrative center of Karachevsky District in Bryansk Oblast, Russia. Population:
History
First chronicled in 1146, it was the capital of one of the Upper Oka Principalities in t ...
. Then Lisowski defeated the front guard of a force several times larger than his own, under the command of knyaz Dmitry Pozharsky
Dmitry Mikhaylovich Pozharsky ( rus, Дми́трий Миха́йлович Пожа́рский, p=ˈdmʲitrʲɪj mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪtɕ pɐˈʐarskʲɪj; 17 October 1577 – 30 April 1642) was a Russian prince known for his military leadershi ...
, who decided to defend instead of attack and fortified his forces in a camp. Lisowczycy broke contact with his forces, burned Belyov
Belyov (russian: Белёв) is a town and the administrative center of Belyovsky District in Tula Oblast, Russia, located on the left bank of the Oka River. Population: 13,180 (2018);
History
As is the case with many other towns in the former Up ...
and Likhvin, took Peremyshl, turned north, defeated the Russian army at Rzhev
Rzhev ( rus, Ржев, p=ˈrʐɛf) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, town in Tver Oblast, Russia, located southwest of Staritsa (town), Tver Oblast, Staritsa and from Tver, on the highway and railway connecting Moscow and Riga. It ...
, proceeded north towards Kashin, burned Torzhok
Torzhok (russian: Торжо́к) is a town in Tver Oblast, Russia, located on the Tvertsa River along the federal highway M10 and a branch of the Oktyabrskaya Railway division of the Russian Railways. The town is famous for its folk craft of g ...
, and returned to Poland heavy with loot without any further opposition from Russian forces. Lisowski and his forces remained at the Russo–Polish border until autumn 1616, at which point Lisowski suddenly fell ill and died on 11 October. The formation was then known as ''Lisowczycy
Lisowczyks or Lisowczycy (; also known as ''Straceńcy'' ('lost men' or 'forlorn hope') or (company of ); or in singular form: Lisowczyk or ) was the name of an early 17th-century irregular unit of the Polish–Lithuanian light cavalry. The Lis ...
''. Despite the death of Lisowski, his forces remained a significant threat: in 1616 they captured Kursk
Kursk ( rus, Курск, p=ˈkursk) is a city and the administrative center of Kursk Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Kur, Tuskar, and Seym rivers. The area around Kursk was the site of a turning point in the Soviet–German stru ...
and defeated Russian forces at Bolkhov
Bolkhov (russian: Бо́лхов) is a town and the administrative center of Bolkhovsky District in Oryol Oblast, Russia, located on the Nugr River (Oka's tributary), from Oryol, the administrative center of the oblast. Population: 12,800 (1 ...
.
The final stage (1617–1618)
 Eventually the Commonwealth Sejm voted to raise the funds necessary to resume large scale military operations. The final attempt by Sigismund and Władysław to gain the throne was a new campaign launched on 6 April 1617. Władysław was the nominal commander, but it was hetman Chodkiewicz who had actual control over the army. In October, the towns of
Eventually the Commonwealth Sejm voted to raise the funds necessary to resume large scale military operations. The final attempt by Sigismund and Władysław to gain the throne was a new campaign launched on 6 April 1617. Władysław was the nominal commander, but it was hetman Chodkiewicz who had actual control over the army. In October, the towns of Dorogobuzh
Dorogobuzh (russian: Дорогобуж) is a historic town and the administrative center of Dorogobuzhsky District in Smolensk Oblast, Russia, straddling the Dnieper River and located east of Smolensk, the administrative center of the oblast. ...
(''Дорогобуж'', ''Drohobuż'', ''Drohobycz'') and Vyazma
Vyazma (russian: Вя́зьма) is a town and the administrative center of Vyazemsky District in Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Vyazma River, about halfway between Smolensk, the administrative center of the oblast, and Mozhaysk. Throu ...
(''Вязьма'', ''Wiaźma'') surrendered quickly, recognizing Władysław as the tsar. However, the Commonwealth forces met stubborn resistance near Mozhaisk
MozhayskAlternative transliterations include ''Mozhaisk'', ''Mozhajsk'', ''Mozhaĭsk'', and ''Možajsk''. ( rus, Можа́йск, p=mɐˈʐajsk) is a town and the administrative center of Mozhaysky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located to th ...
, and Chodkiewicz's plans for a quick advance to Moscow failed. Władysław did not have enough forces to advance to Moscow again, especially because the Russian support for the Poles was all but gone by that time. In 1618 Petro Sahaidachny
Petro Konashevych-Sahaidachny ( uk, Петро Конашевич-Сагайдачний; pl, Piotr Konaszewicz-Sahajdaczny; born about 1582 in Kulchytsi, today Sambir Raion – 20 April 1622 in Kyiv) was a Ukrainian Cossack political and ...
agreed to join the campaign against the Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I i ...
. His army of Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporoz ...
invaded from the South, captured and sacked a number of towns, such as Livny, Yelets, Dankov, etc. and headed for Moscow. The Russian army opposing the Poles retreated to Moscow and on 2 October Chodkiewicz and Sahaidachny together launched a siege of the Russian capital. However, their armies were not ready for a long siege and shortly after the night assault on October 10–11 failed, the siege was lifted. Negotiations began and a peace treaty was signed in December 1618.
Aftermath
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
. On 11 December 1618 the Truce of Deulino
The Truce of Deulino (also known as Peace or Treaty of Dywilino) concluded the Polish–Muscovite War (1609–1618) between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia. It was signed on 11 December 1618 and took effect on 4 Jan ...
, which concluded the Dimitriad's war, gave the Commonwealth control over some of the conquered territories, including the territories of Chernigov
Chernihiv ( uk, Черні́гів, , russian: Черни́гов, ; pl, Czernihów, ; la, Czernihovia), is a List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in northern Ukraine, which serves as the administrative ...
and Severia
Severia or Siveria ( orv, Сѣверія, russian: Северщина, translit=Severshchina, uk, Сіверія or , translit. ''Siveria'' or ''Sivershchyna'') is a historical region in present-day southwest Russia, northern Ukraine, eastern ...
(''Siewiersk'') and the city of Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest c ...
, and proclaimed a 15-year truce
A ceasefire (also known as a truce or armistice), also spelled cease fire (the antonym of 'open fire'), is a temporary stoppage of a war in which each side agrees with the other to suspend aggressive actions. Ceasefires may be between state act ...
. Władysław refused to relinquish his claim to the Russian throne, even though Sigismund had already done so. While the Commonwealth gained some territories in the east, in terms of finance and lives it was a very costly victory.
In 1632 the Truce of Deulino expired, and hostilities immediately resumed in the course of a conflict known as the Smolensk War
The Smolensk War (1632–1634) was a conflict fought between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia.
Hostilities began in October 1632 when Russian forces tried to capture the city of Smolensk. Small military engagements produced mix ...
. This time the war was started by the Russians, who tried to exploit the suspected weakness of the Commonwealth after the unexpected death of Sigismund III. However, they failed to regain Smolensk. Mikhail Shein
Mikhail Borisovich Shein (Михаил Борисович Шеин, ) (late 1570s–1634) was a leading Russian general during the reign of Tsar Mikhail Romanov. Despite his tactical skills and successful military career, he ended up losing his ar ...
surrendered to Władysław IV Władysław is a Polish given male name, cognate with Vladislav. The feminine form is Władysława, archaic forms are Włodzisław (male) and Włodzisława (female), and Wladislaw is a variation. These names may refer to:
Famous people Mononym
* ...
on 1 March 1634, and the Russians accepted the Treaty of Polyanovka
The Treaty of Polyanovka ( pl, Polanów, also known as the ''Peace of Polyanovka / Polanów'') was a peace treaty signed on 14 June 1634 between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia in the village of Semlevo located near ...
in May 1634. The Russians had to pay 20,000 rubles to the Commonwealth, but Władysław relinquished his claim to the Russian throne and recognized Michael as the legitimate tsar of Russia, also returning the Russian royal insignia.
Modern legacy
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
's Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
and other Axis Powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
could not manage. In Russia it was useful to the new dynasty of tsars, the Romanovs
The House of Romanov (also transcribed Romanoff; rus, Романовы, Románovy, rɐˈmanəvɨ) was the reigning imperial house of Russia from 1613 to 1917. They achieved prominence after the Tsarina, Anastasia Romanova, was married to t ...
, who understood that history is a powerful political tool, written by the victors. They tried to erase all references and theories to their role in creating the False Dmitrys, self-interested cooperation with Polish and Swedish interventions, or their opposition to the liberal '' unia troista''; instead they supported a portrayal of Dmitriads as the heroic defense of Russian nation against the barbaric invasion of Polish–Jesuit alliance, who attempted to destroy the Russian Orthodox culture. This was the history line shown by the famous Russian historian, Nikolai Mikhailovich Karamzin
Nikolay Mikhailovich Karamzin (russian: Николай Михайлович Карамзин, p=nʲɪkɐˈlaj mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪtɕ kərɐmˈzʲin; ) was a Russian Imperial historian, romantic writer, poet and critic. He is best remembered for ...
, beautifully described by Aleksandr Pushkin
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin (; rus, links=no, Александр Сергеевич ПушкинIn pre-Revolutionary script, his name was written ., r=Aleksandr Sergeyevich Pushkin, p=ɐlʲɪkˈsandr sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈpuʂkʲɪn, ...
in his "Boris Godunov" and by Modest Mussorgsky
Modest Petrovich Mussorgsky ( rus, link=no, Модест Петрович Мусоргский, Modest Petrovich Musorgsky , mɐˈdɛst pʲɪˈtrovʲɪtɕ ˈmusərkskʲɪj, Ru-Modest Petrovich Mussorgsky version.ogg; – ) was a Russian compo ...
in his opera
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librett ...
''Boris Godunov'', and later romanticized in the film '' Minin and Pozharsky'' by Vsevolod Pudovkin. The Monument to Minin and Pozharsky
The Monument to Minin and Pozharsky (russian: Па́мятник Ми́нину и Пожа́рскому) is a bronze statue designed by Ivan Martos and located on the Red Square in Moscow, Russia, in front of Saint Basil's Cathedral. The statue ...
was erected in Moscow's Red Square in 1818. The communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a s ...
regime of the Soviet Union also found this war a useful propaganda tool, especially during the times of the Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (Polish–Bolshevik War, Polish–Soviet War, Polish–Russian War 1919–1921)
* russian: Советско-польская война (''Sovetsko-polskaya voyna'', Soviet-Polish War), Польский фронт (' ...
. The Dymitriads were also useful for the propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded ...
of Józef Piłsudski
), Vilna Governorate, Russian Empire (now Lithuania)
, death_date =
, death_place = Warsaw, Poland
, constituency =
, party = None (formerly PPS)
, spouse =
, children = Wan ...
's Polish government between the World Wars.
In post-Soviet Russia
The post-Soviet states, also known as the former Soviet Union (FSU), the former Soviet Republics and in Russia as the near abroad (russian: links=no, ближнее зарубежье, blizhneye zarubezhye), are the 15 sovereign states that wer ...
the only autumn holiday, the National Unity Day, first celebrated on 4 November 2005, commemorates the popular uprising that ejected the occupying force from Moscow in November 1612, and more generally the end of the Time of Troubles and foreign interventions in Russia. Its name alludes to the idea that all the classes of the Russian society willingly united to preserve the Russian statehood when its demise seemed inevitable, even though there was neither Tsar nor Patriarch to guide them.
See also
* Prince Władysław's March on Moscow *Livonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) was the Russian invasion of Old Livonia, and the prolonged series of military conflicts that followed, in which Tsar Ivan the Terrible of Russia (Muscovy) unsuccessfully fought for control of the region (pre ...
(1577–1582)
* Moldavian Magnate Wars
The Moldavian Magnate Wars, or Moldavian Ventures, refer to the period at the end of the 16th century and the beginning of the 17th century when the magnates of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth intervened in the affairs of Moldavia, clashing ...
(1593–1621)
* Time of Troubles
The Time of Troubles (russian: Смутное время, ), or Smuta (russian: Смута), was a period of political crisis during the Tsardom of Russia which began in 1598 with the death of Fyodor I (Fyodor Ivanovich, the last of the Rurik dy ...
(1598–1615)
* Zebrzydowski rebellion (1606–1608)
* The De la Gardie Campaign (1609–1610)
** Ingrian War
The Ingrian War ( sv, Ingermanländska kriget) between the Swedish Empire and the Tsardom of Russia lasted between 1610 and 1617. It can be seen as part of Russia's Time of Troubles and is mainly remembered for the attempt to put a Swedish duke ...
(1610–1617)
* Treaty of Stolbovo
The Treaty of Stolbovo () was a peace treaty that ended the Ingrian War (), which had been fought between the Swedish Empire and the Russian Tsardom between 1610 and 1617.
History
After nearly two months of negotiations, representatives from Swe ...
(1617)
* Polish–Swedish wars
The Polish–Swedish Wars were a series of wars between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Sweden. Broadly construed, the term refers to a series of wars between 1563 and 1721. More narrowly, it refers to particular wars between 1600 and ...
(1600–1611, 1617–1629)
** Smolensk War
The Smolensk War (1632–1634) was a conflict fought between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia.
Hostilities began in October 1632 when Russian forces tried to capture the city of Smolensk. Small military engagements produced mix ...
(1632–1634)
* Treaty of Polanów
The Treaty of Polyanovka ( pl, Polanów, also known as the ''Peace of Polyanovka / Polanów'') was a peace treaty signed on 14 June 1634 between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia in the village of Semlevo located near ...
(1634)
* 1612, a Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
epic drama
Drama is the specific mode of fiction represented in performance: a play, opera, mime, ballet, etc., performed in a theatre, or on radio or television.Elam (1980, 98). Considered as a genre of poetry in general, the dramatic mode has been ...
film released on 1 November 2007 about the expulsion of Polish troops from Moscow
References
Sources
*Norman Davies
Ivor Norman Richard Davies (born 8 June 1939) is a Welsh-Polish historian, known for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland and the United Kingdom. He has a special interest in Central and Eastern Europe and is UNESCO Professor at ...
, ''God's Playground'', and (two volumes).
* Andrzej NowakPolacy na Kremlu
Tygodnik "Wprost", Nr 1182 (31 lipca 2005), , accessed on 29 July 2005 *
Paweł Jasienica
Paweł Jasienica was the pen name of Leon Lech Beynar (10 November 1909 – 19 August 1970), a Poles, Polish historian, journalist, essayist and soldier.
During World War II, Jasienica (then, Leon Beynar) fought in the Polish Army, and later, ...
, ''Rzeczpospolita Obojga Narodów'', .
* Jerzy Malec
Jerzy is the Polish language, Polish version of the masculine given name George (given name), George. The most common nickname for Jerzy is Jurek (given name), Jurek (), which may also be used as an official first name. Occasionally the nickname Je ...
, ''Szkice z dziejów federalizmu i myśli federalistycznej w czasach nowożytnych'', Wydawnictwo UJ, 1999,
* Chester S. L. Dunning, ''Russia's First Civil War: The Time of Troubles and the Founding of the Romanov Dynasty'', Pennsylvania State University Press, 2001, (parts available for free on Google Print
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical ...
)
Further reading
* Henryk Wisner, ''Król i car: Rzeczpospolita i Moskwa w XVI i XVII wieku'' (''King and Tsar: Republic and Moscow in 16th and 17th Centuries''), Książka i Wiedza, Warszawa, 1995, * Robert Szcześniak, ''Kłuszyn 1610'', Bellona Dom Wydawniczy, 2004 *Tomasz Bohun Tomasz is a Polish given name, the equivalent of Thomas in English.
Notable people with the given name include:
*Tomasz Adamek (born 1976), Polish heavyweight boxer
*Tomasz Arciszewski (1877–1955), Polish socialist politician and Prime Minist ...
, ''Moskwa 1612'', Bellona Dom Wydawniczy, 2005,
* ''Moskwa w rękach Polaków. Pamiętniki dowódców i oficerów garnizonu w Moskwie'' (''Moscow in Polish Hands: Memoires of Commanders and Officers of the Moscow Garrison''). Platan, 2005,
External links
Polish occupation of Russia
!--404 now--> {{DEFAULTSORT:Polish-Muscovite War (1605-18) 1600s in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth 1600s in Russia 1610s in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth 1610s in Russia 17th-century conflicts Invasions of Russia Wars involving Russia Wars involving the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth Polish–Russian wars Warfare of the Early Modern period Wars of succession involving the states and peoples of Europe Time of Troubles